The business world today moves faster than ever. Markets shift in weeks, customer expectations evolve in real time, and even small inefficiencies can quietly drain millions each year. In such an environment, operational agility is not just an advantage; it is essential for survival.
AI agents are transforming how enterprises handle routine, repetitive work. Tasks that once consumed hours, like responding to customer inquiries, processing returns, or managing standard workflows, can now be completed in seconds with unmatched speed, accuracy, and consistency. By automating these day-to-day operations, AI agents free human teams to focus on higher-value work where judgment, creativity, and strategic thinking matter most.
Take AI in customer services support as an example: a single AI agent can autonomously handle the entire spectrum of inquiries from product information to return requests, personalizing each interaction, reducing waiting times, and lowering operational costs. For enterprises that embrace this shift, the impact is immediate and measurable: millions saved through leaner processes, faster time-to-market, and the agility to turn disruption into opportunity. For those who hesitate, the risk is falling behind competitors who act faster, losing market share, and missing the moments that can redefine their business.
In this blog, we’ll explore what AI agents are, how they function, and why their strategic deployment can save millions while transforming the way your enterprise competes in an AI-driven world.
Demystifying AI agents for business leaders
AI agents represent a groundbreaking advancement in artificial intelligence, designed to act autonomously within specific business environments to achieve complex objectives. These autonomous systems independently make decisions and take actions with minimal or no human intervention.
Leveraging the latest advancements in reasoning AI models, AI agents analyze complex tasks by breaking them down, systematically exploring multiple pathways to identify and test solutions, ultimately delivering successful outcomes. They operate within precise boundaries while continuously adapting to evolving conditions, enabling smarter, faster problem-solving tailored to dynamic business needs.
Built on foundational artificial intelligence technologies such as machine learning and natural language processing, AI agents extend the capabilities of conventional AI applications. Unlike conventional Gen AI solutions that handle narrow, predefined tasks, AI agents orchestrate entire end-to-end processes autonomously. Their advanced reasoning, adaptive learning, and collaborative capabilities transform them from simple tools into intelligent partners, driving enhanced enterprise productivity, efficiency, and strategic growth.
What makes an AI agent truly “agentic”
AI agents earn the designation of “agentic” when they demonstrate the capabilities that allow them to operate autonomously, purposefully, and reliably in complex enterprise environments. These defining traits enable organizations to scale operations, optimize processes, and respond dynamically to rapidly changing conditions.
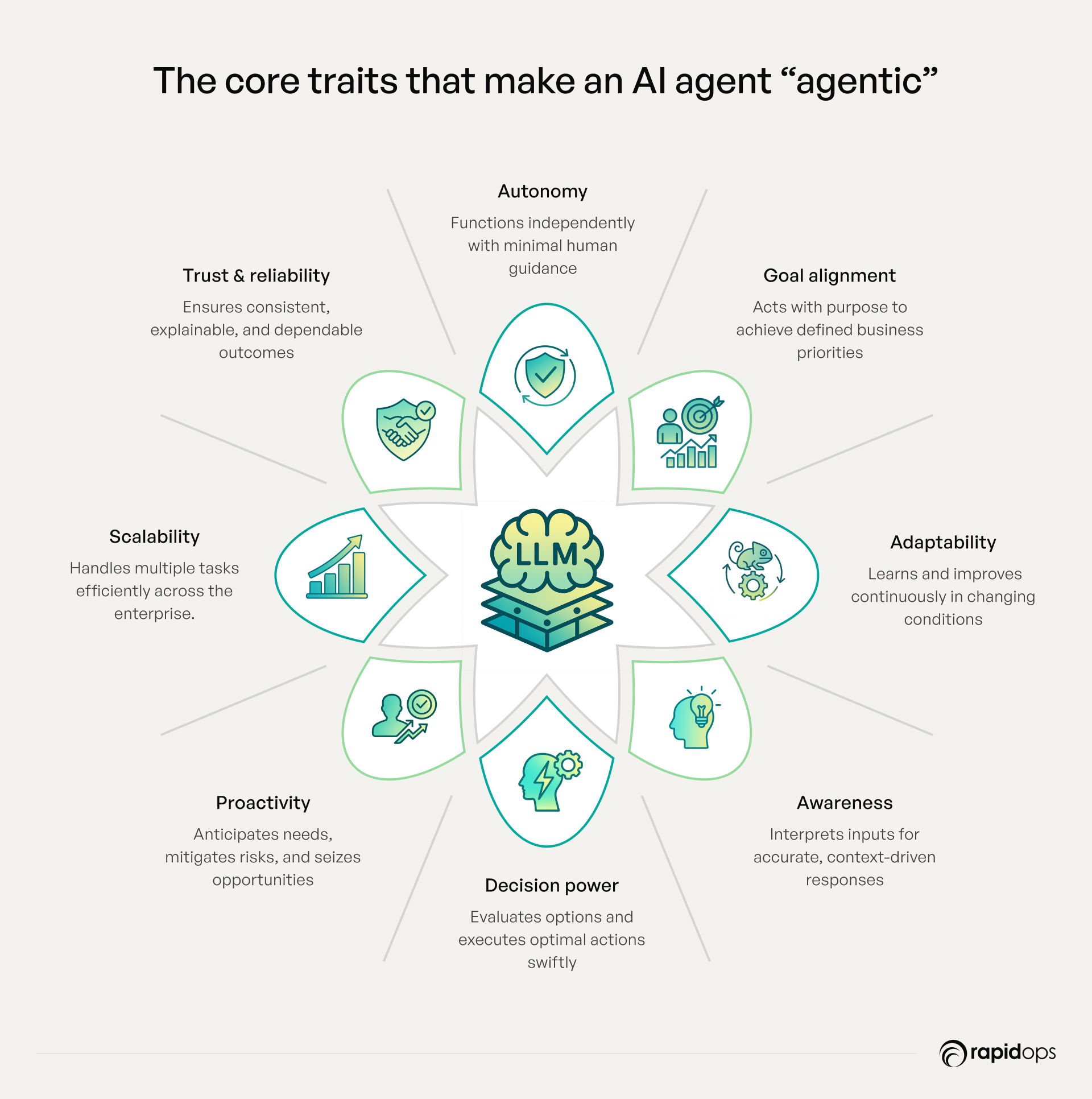
- Autonomy: AI agents function independently with minimal human guidance, reducing reliance on manual intervention while maintaining operational continuity.
- Goal orientation: They act with purpose, consistently aligning actions to achieve clearly defined business objectives and strategic priorities.
- Adaptability and learning: By continuously analyzing data and outcomes, AI agents improve over time, refining performance and decision quality in response to evolving conditions.
- Perception and environmental awareness: AI agents sense and interpret diverse inputs from their environment, ensuring contextually informed and relevant responses.
- Decision-making capability: They evaluate options and select optimal actions efficiently, enabling the timely execution of complex workflows across the enterprise.
- Proactivity: Rather than merely reacting, AI agents initiate actions that anticipate operational needs, mitigating risks and identifying opportunities ahead of time.
- Communication & interaction: They seamlessly engage with other systems, agents, or humans, facilitating coordinated, multi-layered operations.
- Scalability: Capable of managing multiple tasks or processes simultaneously, AI agents maintain efficiency at enterprise scale.
- Reliability & consistency: AI agents execute tasks accurately and dependably over time, ensuring predictable outcomes across high-volume operations.
- Transparency & explainability: Their actions and decisions are traceable and interpretable, providing executives with insights necessary for governance, compliance, and strategic confidence.
Understanding these traits positions AI agents as drivers of enterprise efficiency and strategic growth, enabling organizations to respond swiftly to change and focus resources on initiatives that deliver the highest impact.
What is the difference between AI agents, AI assistants, and chatbots?
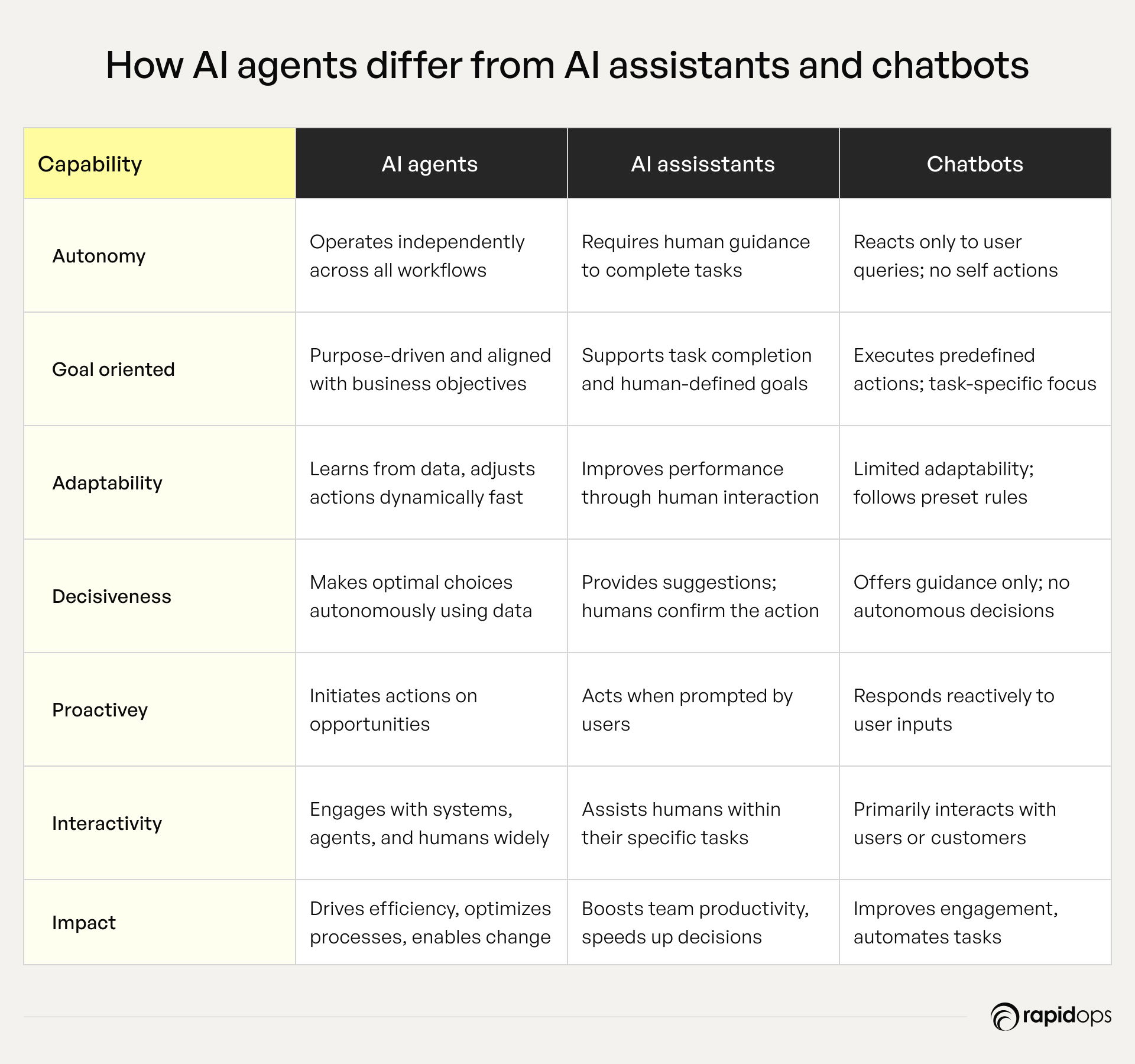
Enterprises today deploy AI in multiple forms, each with distinct capabilities, purposes, and strategic impacts. Understanding these differences is essential for executives seeking to leverage AI agent development effectively. While all three systems harness artificial intelligence, their level of autonomy, decision-making ability, and enterprise impact vary significantly, influencing where and how they should be applied.
AI agents
AI agents are autonomous and adaptive entities capable of performing tasks, interacting with multiple systems, and responding to changes in real time with minimal human oversight. They operate continuously, coordinating across workflows and making context-aware decisions to achieve defined objectives.
In enterprises, AI agents can handle complex, end-to-end processes such as supply chain optimization, risk monitoring, or financial reconciliation, delivering precision and scale that go far beyond traditional automation.
AI assistants
AI assistants are designed to support individuals or teams with specific, task-oriented functions. They typically work within narrower boundaries, helping users schedule meetings, summarize documents, draft communications, or surface relevant insights on demand.
While more flexible than chatbots, they are largely user-driven, acting as digital helpers rather than fully independent operators. Their strength lies in improving productivity and reducing routine workload, but they do not replace enterprise-scale process execution.
Chatbots
Chatbots are primarily conversational tools built to interact with users through text or voice. Most are designed to follow pre-defined rules or scripts, answering customer queries, guiding website navigation, or handling basic service requests.
Even when enhanced with natural language processing, chatbots remain reactive; they respond to prompts but do not operate autonomously. Their value lies in customer engagement and service efficiency, but they lack the adaptive intelligence and operational depth of AI agents or even assistants.
Evolution of AI agents in enterprises
AI agents have undergone a significant transformation, evolving from simple automation tools to sophisticated, autonomous systems that drive strategic business outcomes. Understanding this evolution is crucial for senior leaders aiming to leverage AI for competitive advantage.
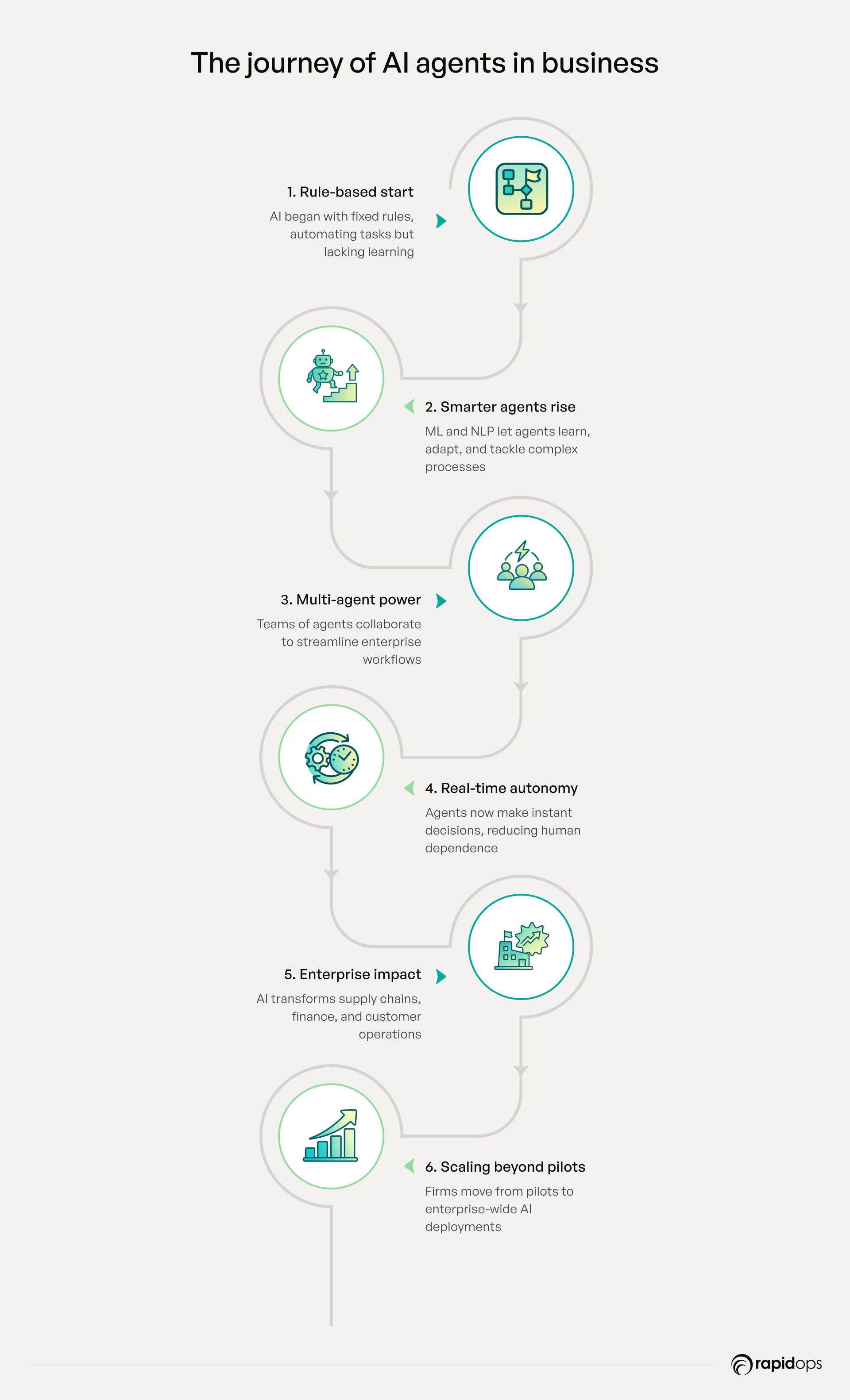
1. Early AI models: Rule-based and task-specific automation
In the early stages, AI models were primarily rule-based, executing predefined tasks without the ability to learn or adapt. These systems were effective for automating repetitive processes but lacked flexibility and scalability.
2. Transition to intelligent, adaptive agents
Advancements in machine learning and natural language processing enabled AI agents to learn from data and adapt their behavior over time. This shift allowed for more dynamic and responsive systems capable of handling complex tasks and making informed decisions.
3. Emergence of multi-agent systems for complex enterprise workflows
As business processes became more intricate, organizations adopted multi-agent AI systems where multiple AI agents collaborate to achieve common goals. This approach enhanced efficiency and coordination across various functions within the enterprise.
4. Adoption of autonomous decision-making in operations
Modern AI agents are equipped with advanced reasoning capabilities, enabling them to make autonomous decisions in real-time. This autonomy reduces the need for human intervention, streamlining operations and accelerating decision-making processes.
5. Expansion into enterprise-wide applications
AI agents have expanded beyond isolated applications to become integral components of enterprise-wide systems. They now play a pivotal role in areas such as supply chain management, customer service, and financial operations, driving significant improvements in efficiency and effectiveness.
6. Shift from pilot projects to scalable enterprise deployment
Organizations are moving from experimental pilot projects to large-scale deployment of AI agents. This shift is facilitated by advancements in AI infrastructure and platforms that support seamless integration and scalability across the enterprise.
Components of AI agents
AI agents function through a set of interconnected components that enable them to perceive, reason, act, learn, and collaborate autonomously. Understanding these core components is crucial for business leaders seeking to leverage AI agents to enhance operational efficiency, lower costs, and gain a competitive edge.
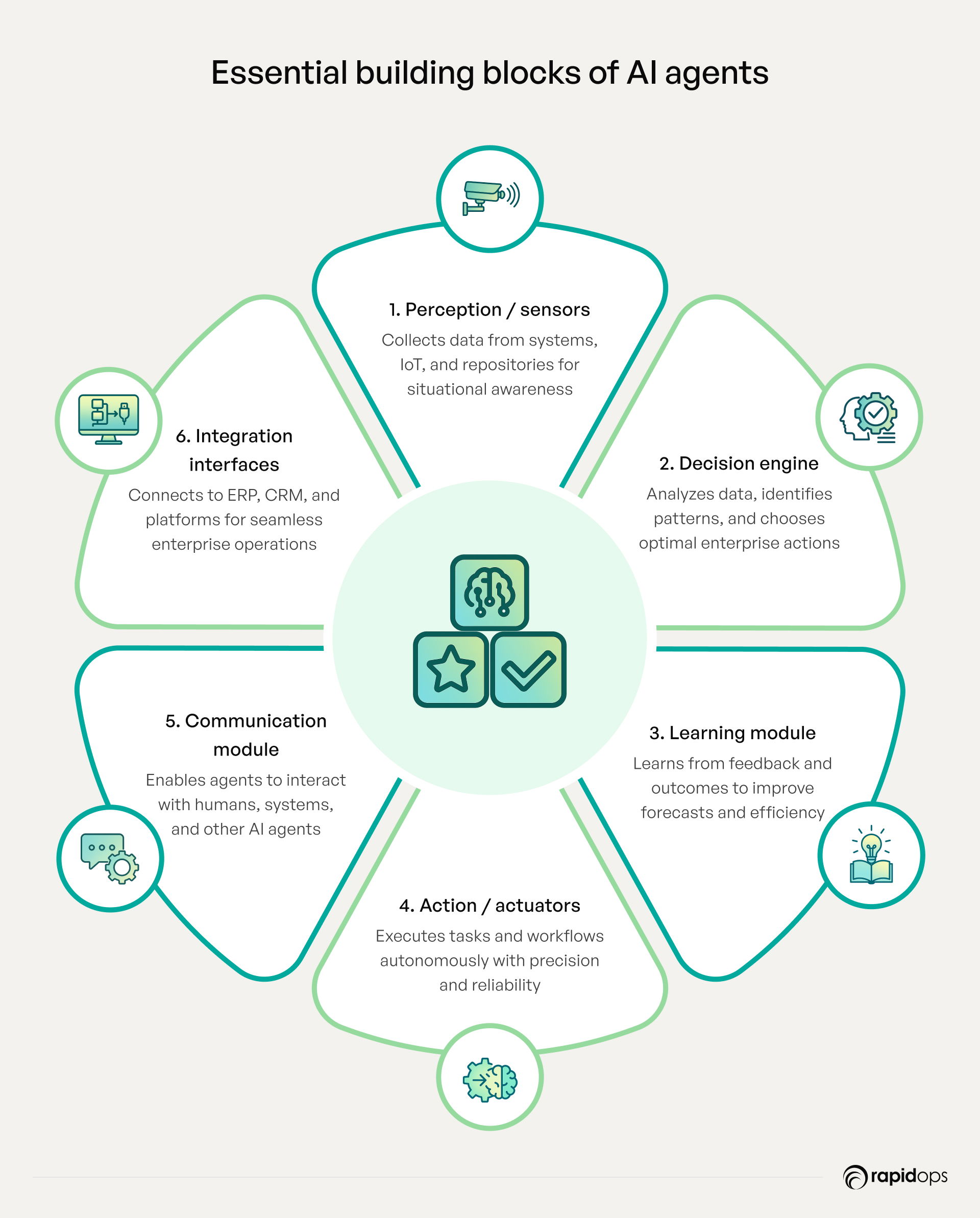
1. Perception/sensors
Perception forms the foundation of AI agents. Through advanced sensors and data ingestion mechanisms, agents continuously collect information from various sources, including enterprise systems, external knowledge repositories, databases, IoT devices, and other structured or unstructured data sources. This input allows agents to maintain situational awareness, detect anomalies, and respond dynamically to evolving operational, customer, or market conditions.
2. Decision engine/reasoning
The decision engine is the analytical core of AI agents. Leveraging sophisticated reasoning algorithms, AI models, and access to institutional knowledge, it evaluates data, identifies patterns, and determines optimal actions aligned with enterprise objectives. This ensures decisions are both accurate and strategically aligned with organizational goals.
3. Learning module
The learning module enables AI agents to continually refine their performance. Through machine learning and feedback loops, agents adapt based on historical data, real-time outcomes, and user interactions. This capability ensures evolving accuracy, smarter forecasts, and higher operational efficiency over time.
4. Actuators/action module
Actuators translate decisions into actions. Whether updating records, orchestrating workflows, or executing autonomous operational tasks, agents perform with precision and reliability, reducing manual intervention while ensuring consistent outcomes.
5. Communication module
Effective collaboration requires clear communication. This module enables agents to interact with human teams, other AI agents, or connected systems, maintaining alignment with enterprise goals and ensuring transparency in actions and decisions.
6. Integration interfaces
Integration interfaces connect AI agents to ERP, CRM, analytics platforms, databases, and other enterprise systems. These connections provide seamless access to institutional knowledge, rules, and operational workflows, enabling agents to function effectively within existing IT environments.
How AI agents work
AI agents operate through a structured cycle that enables enterprises to process data, plan actions, execute tasks, learn from outcomes, and collaborate across teams. Understanding this cycle allows leaders to identify precisely where AI agents can streamline workflows, enhance customer interactions, and deliver tangible business value.
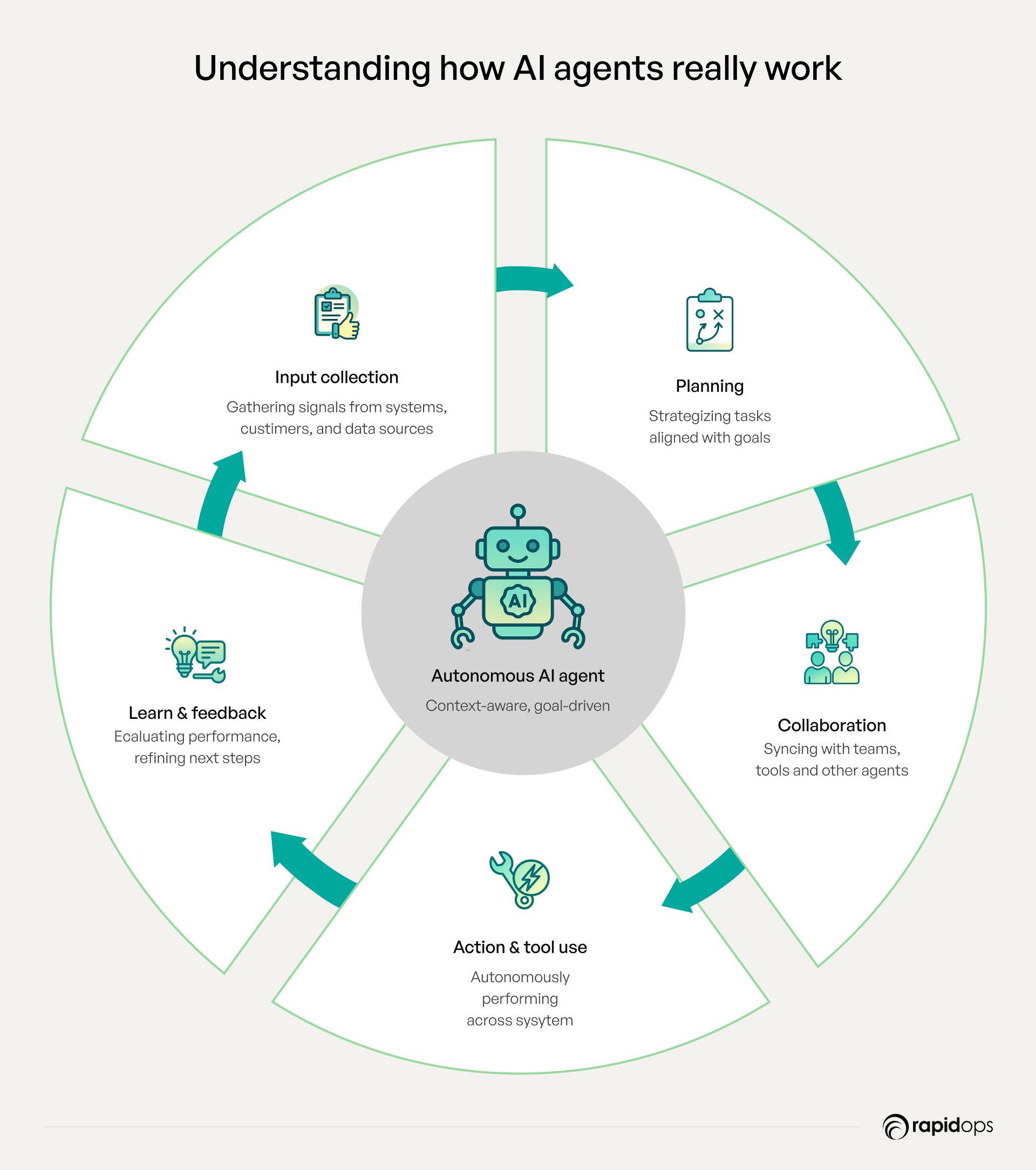
1. Input collection
Agents begin by collecting inputs from diverse sources, including customer interactions, enterprise systems, and operational metrics. Comprehensive data collection ensures that agents have the context needed to make informed decisions. When a customer submits a query about an order, the agent gathers account details, purchase history, and prior interactions to establish a complete picture that guides accurate resolution.
2. Planning
With inputs collected, the agent evaluates possible actions, identifies dependencies, and sequences tasks to align with business priorities. This planning ensures workflows are executed efficiently and critical issues are addressed promptly. For instance, the agent decides whether the customer query can be answered using the knowledge base or requires escalation to a human support agent.
3. Action
Agents then act independently, orchestrating processes across systems and teams without continuous human intervention. Autonomous execution accelerates response times, reduces errors, and ensures consistency in outcomes. The agent responds directly to the customer query, providing a personalized solution while updating systems and notifying relevant teams.
4. Learning
AI agents analyze results, incorporate feedback, and refine strategies to improve effectiveness, accuracy, and adaptability over time. This continuous learning loop ensures long-term operational resilience. After resolving the query, the agent evaluates customer satisfaction and adjusts future responses to handle similar inquiries more effectively.
5. Collaboration
Agents collaborate with other agents, enterprise systems, or human teams to achieve multi-step objectives seamlessly. This coordination supports alignment, scalability, and operational continuity. If escalation is needed, the agent provides full context to a human support agent, enabling rapid, informed decision-making.
Types of AI agents
AI agents can be classified into distinct types based on their decision-making capabilities, autonomy, and interaction with humans or systems. Understanding these types helps leaders select the right AI approach for enterprise applications, whether for automating processes, managing complex workflows, or supporting strategic decision-making.
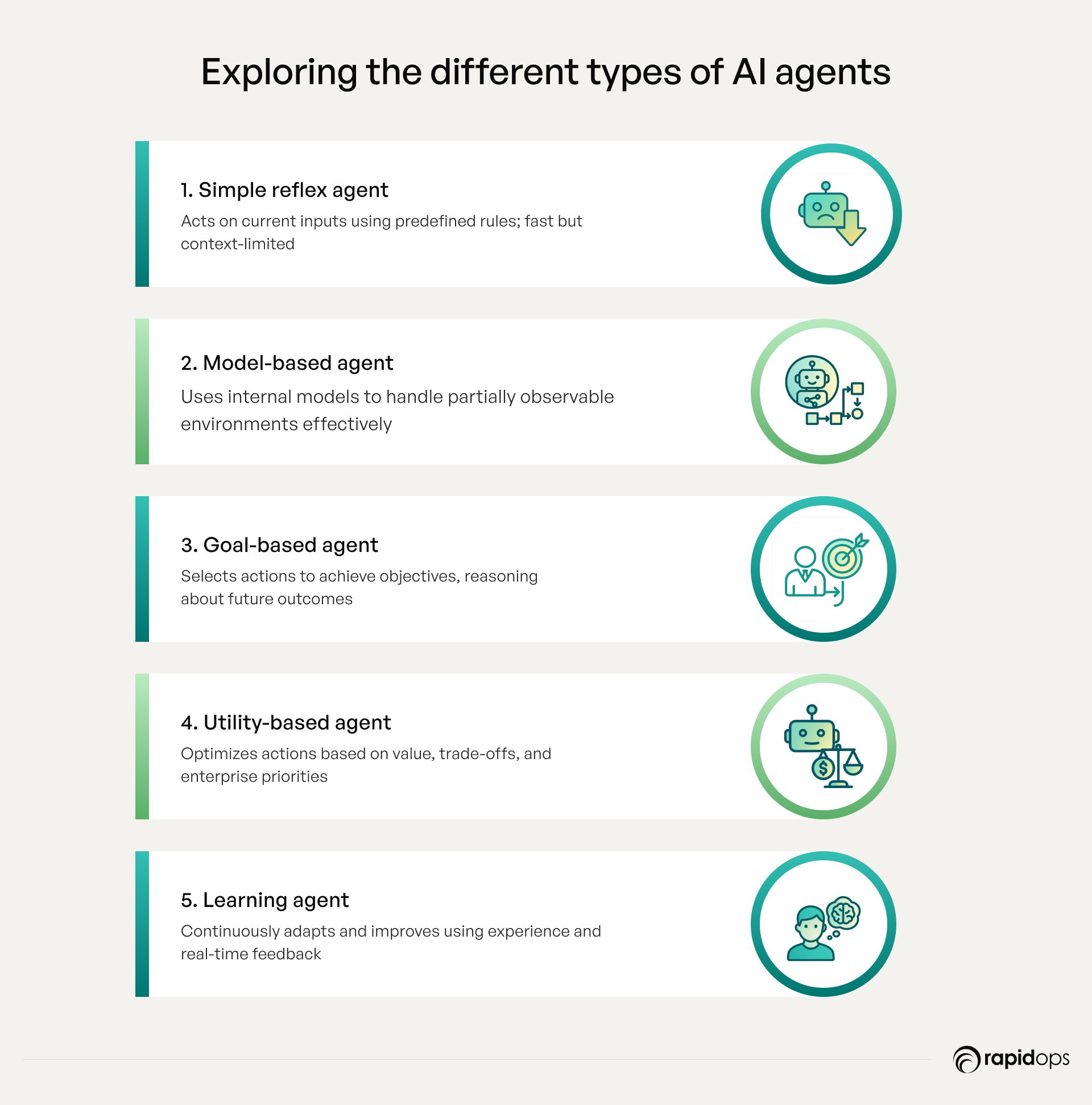
1. Simple reflex agents
Simple reflex agents operate on a stimulus-response basis. They act solely on the current percept, following pre-defined rules, without considering past states or outcomes. While fast and efficient for structured, predictable tasks, they are limited in dynamic environments where context or history matters. Use cases include rule-based chatbots or automated sensor monitoring systems.
2. Model-based reflex agents
Model-based reflex agents maintain an internal model of the environment to handle partially observable scenarios. By storing state information, these agents can make informed decisions based on both current percepts and prior knowledge. This type is suited for enterprise processes requiring consistent performance in evolving conditions, such as supply chain monitoring or predictive maintenance.
3. Goal-based agents
Goal-based agents select actions to achieve specific objectives rather than simply responding to stimuli. They evaluate future states, reasoning about which actions will lead to desired outcomes. Enterprises leverage goal-based agents for strategic planning, route optimization, or intelligent recommendation engines, where multiple potential paths exist.
4. Utility-based agents
Utility-based agents go beyond goal achievement by quantifying preferences and measuring the “utility” of different outcomes. They optimize actions to maximize overall value, factoring in trade-offs and risks. These agents are ideal for complex decision-making scenarios, such as pricing strategies, portfolio management, and resource allocation in large-scale operations.
5. Learning agents
Learning agents continuously improve their performance by learning from experiences and feedback. They adapt to changing environments and refine strategies over time, making them indispensable in AI-driven enterprises that require dynamic problem-solving. Applications include personalized marketing, predictive analytics, autonomous systems, and AI-powered customer intelligence platforms.
Selecting the right AI agent type is crucial for achieving enterprise success. By aligning agent capabilities, whether reflex, model-based, goal-driven, utility-based, or learning, with business needs and complexity, organizations can unlock efficiency, insight, and innovation at scale.
What value AI agents are unlocking for businesses
Envision an enterprise where every process operates with speed, precision, and autonomous control. AI agents make this possible by executing time-intensive tasks with the highest quality, accelerating workflows, and amplifying decision-making capabilities, unlocking measurable value across operations, customer engagement, and innovation.
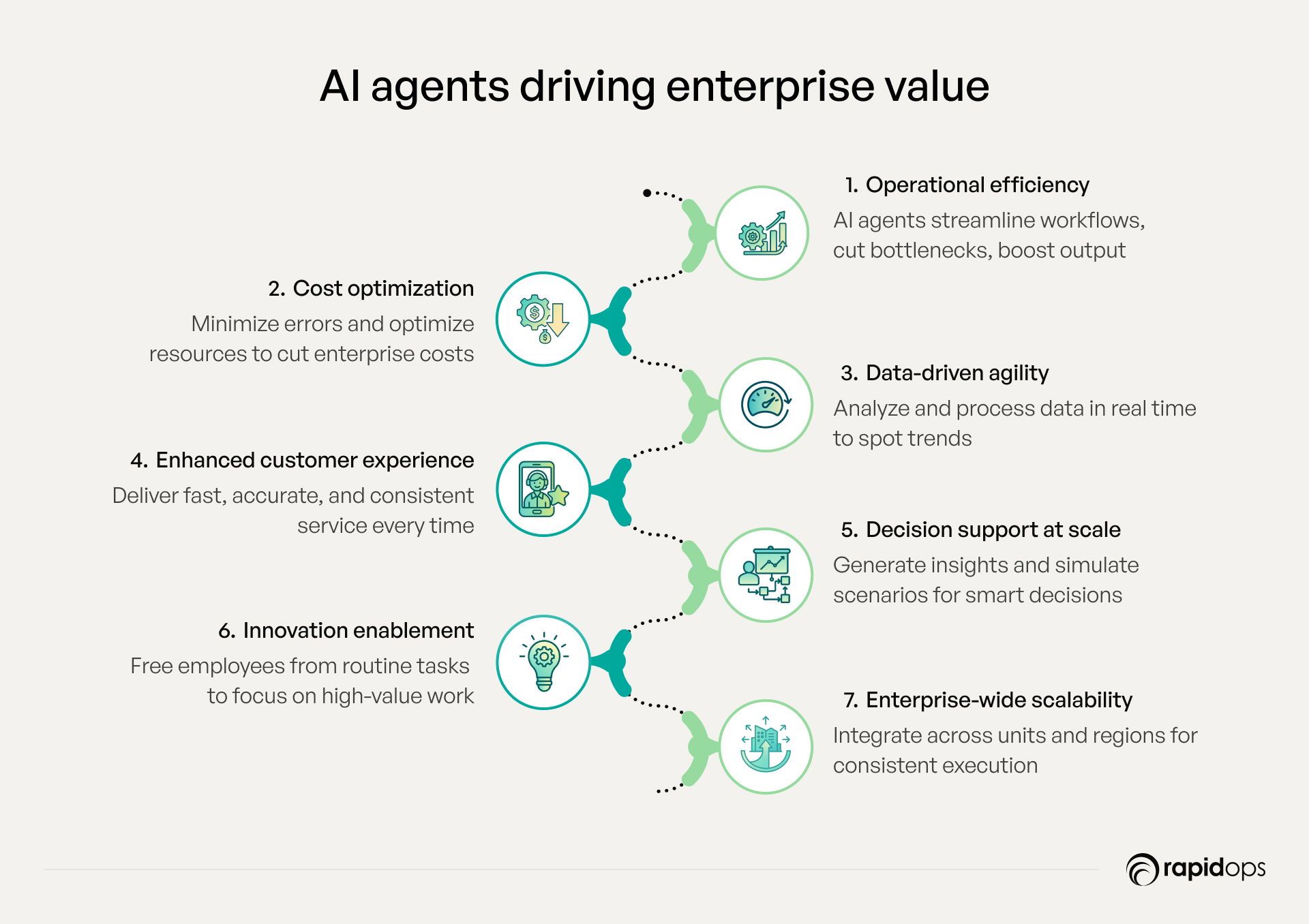
1. Operational efficiency
AI agents autonomously prioritize, orchestrate, and execute workflows across systems, eliminating bottlenecks and repetitive manual tasks. By maintaining consistent precision and high-quality execution, they accelerate throughput and ensure reliable outcomes at scale.
2. Cost optimization
Through automated task execution and resource allocation, AI agents minimize human intervention, prevent errors, and optimize utilization. These capabilities directly reduce operational costs, enhance margins, and sustain high performance across enterprise functions.
3. Data-driven agility
AI agents process and analyze structured and unstructured data in real time, detecting patterns, forecasting demand, and anticipating disruptions. Their speed and analytical rigor allow enterprises to adapt processes immediately, respond proactively, and maintain continuity in dynamic environments.
4. Enhanced customer experience
By autonomously managing interactions and tasks, AI agents deliver fast, accurate, and consistent outputs. Their efficiency and precision ensure high-quality service delivery, improving responsiveness, reliability, and overall customer satisfaction.
5. Decision support at scale
AI agents handle complex analytical workloads, generating actionable insights, simulating scenarios, and evaluating performance metrics to inform decision-making. By accelerating these time-consuming processes, executives can make faster, data-driven decisions while maintaining strategic alignment.
6. Innovation enablement
By automating routine and repetitive operational tasks, AI agents enable employees to focus on high-value strategic initiatives, such as product innovation and process optimization. This synergy of human creativity and AI-driven efficiency accelerates enterprise innovation and ensures consistent execution.
7. Enterprise-wide scalability
AI agents integrate seamlessly across departments, geographies, and business units, ensuring uniform execution and high-quality performance. Their autonomous capabilities allow enterprises to scale operations efficiently while maintaining governance, compliance, and strategic alignment.
How AI agents are transforming business operations
Businesses face rising complexity, slow processes, and evolving customer expectations. AI agents streamline workflows, anticipate disruptions, and deliver actionable insights, enabling leaders to enhance responsiveness, reduce risk, and drive strategic growth with measurable impact.
1. Dynamic pricing optimization
AI agents enable enterprises to adjust pricing in real time based on demand fluctuations, competitor actions, and inventory levels. Unlike static models, agents continuously analyze market signals, customer behavior, and contextual data to identify the most profitable price point. This dynamic approach enables companies to maximize margins during peak demand while maintaining competitive prices in low-demand scenarios. For leaders, this means leveraging pricing as a strategic growth tool, driving higher revenue, enhancing market responsiveness, and maintaining customer trust in increasingly volatile markets.
2. Personalized product recommendations
AI agents deliver highly personalized recommendations by analyzing customer profiles, purchase history, browsing patterns, and contextual interactions. Unlike generic recommendation engines, agents continuously adapt, learning from each engagement to refine suggestions across both digital and physical touchpoints. This personalization enhances conversion rates, increases basket size, and improves long-term loyalty. For enterprises, this means transforming product discovery into a personalized experience that drives revenue and fosters brand differentiation. Leaders can view agents as a scalable capability that aligns offerings with individual customer expectations in real time.
3. Personalized customer service
AI agents elevate customer service from reactive to proactive by handling queries, resolving issues, and guiding customers across multiple channels with contextual intelligence. They integrate knowledge bases, transaction histories, and real-time data to provide accurate and consistent support without delays. This reduces call center volumes, lowers service costs, and enhances customer satisfaction. For decision-makers, deploying AI agents in customer service means unlocking 24/7 scalability, ensuring personalized experiences, and freeing human representatives to focus on complex, high-value interactions that require empathy and judgment.
4. Inventory management
AI agents transform inventory management by monitoring demand signals, supplier performance, and logistics data in real time. They dynamically adjust stock levels, predict shortages, and recommend replenishments before disruptions occur. Unlike traditional systems, agents adapt continuously to changing supply chain conditions, ensuring an optimal balance between cost efficiency and product availability. For enterprises, this means reducing carrying costs, minimizing stockouts, and creating resilient supply chains. Leaders gain a data-driven capability to align inventory strategies with market demand and operational agility at scale.
5. Predictive equipment maintenance
AI agents analyze sensor data, usage patterns, and environmental conditions to predict equipment failures before they occur. By scheduling maintenance proactively, agents reduce unplanned downtime, extend the lifespan of their assets, and lower repair costs. Unlike time-based schedules, predictive maintenance ensures resources are allocated only when necessary, optimizing workforce and capital efficiency. For leaders, this represents a shift from reactive firefighting to proactive asset management, creating safer, more reliable operations while unlocking measurable savings and maintaining uninterrupted service delivery across mission-critical environments.
6. Quality control inspection
AI agents enhance quality control by detecting anomalies, defects, or compliance deviations across manufacturing lines using image recognition, sensor data, and contextual analytics. Unlike manual inspection, which is time-consuming and prone to error, agents provide continuous, objective, and high-speed evaluations. They not only flag issues but also learn from patterns to prevent future defects. For decision-makers, this capability translates into higher production accuracy, reduced waste, regulatory compliance, and consistent customer trust, positioning quality assurance as a proactive value driver rather than a cost center.
7. Production schedule optimization
AI agents dynamically optimize production schedules by analyzing order volumes, labor availability, machine capacity, and supply chain constraints to ensure efficient resource allocation. Unlike static planning tools, agents adapt instantly to disruptions such as material delays or sudden demand surges, ensuring minimal downtime and balanced workloads. This agility improves throughput, reduces operational bottlenecks, and ensures on-time delivery. For leaders, production schedule optimization with AI agents offers a strategic capability to align operations with real-time market needs, enhancing efficiency, flexibility, and profitability across manufacturing and distribution ecosystems.
8. Delivery route optimization
AI agents optimize delivery routes by analyzing real-time traffic conditions, fuel costs, delivery windows, and fleet availability. Unlike static routing software, they continuously adapt to changing conditions, such as accidents, weather disruptions, or changes in customer locations. This reduces travel time, lowers logistics costs, and ensures timely deliveries with a minimal carbon footprint. For enterprises, route optimization not only enhances efficiency but also strengthens customer satisfaction. Leaders can leverage this as a competitive differentiator in supply chain performance and sustainability.
9. Invoice generation
AI agents automate the end-to-end invoice process, integrating sales, inventory, and financial data to ensure accuracy, compliance, and timely delivery. By reducing manual intervention, agents accelerate billing cycles, minimize errors, and enhance cash flow visibility. This enables finance teams to focus on strategic initiatives rather than routine tasks. For leaders, AI-driven invoice generation transforms a traditionally repetitive process into a scalable, insight-driven operation, improving operational efficiency, strengthening vendor and customer trust, and supporting enterprise-wide financial governance and performance.
10. Demand sensing and redistribution
AI agents sense demand shifts by analyzing POS data, market signals, promotions, and external factors such as weather or events. They dynamically adjust supply distribution, ensuring products are allocated to the right locations before shortages or surpluses occur. Unlike traditional forecasting, agents operate in near real time, minimizing waste and lost sales. For leaders, demand sensing with AI agents ensures better alignment between supply and market needs, creating agile, demand-driven operations that strengthen resilience, responsiveness, and customer satisfaction.
100 proven AI agent use cases delivering immediate impact, without the need for massive technology overhauls!
Download Now
Things to consider when implementing AI agents
Implementing AI agents is not merely a technological upgrade; it is a strategic transformation that redefines operations, accelerates decision-making, and drives measurable enterprise impact. For leaders, careful consideration across multiple dimensions ensures that AI agents deliver maximum value while mitigating operational, strategic, and ethical risks.
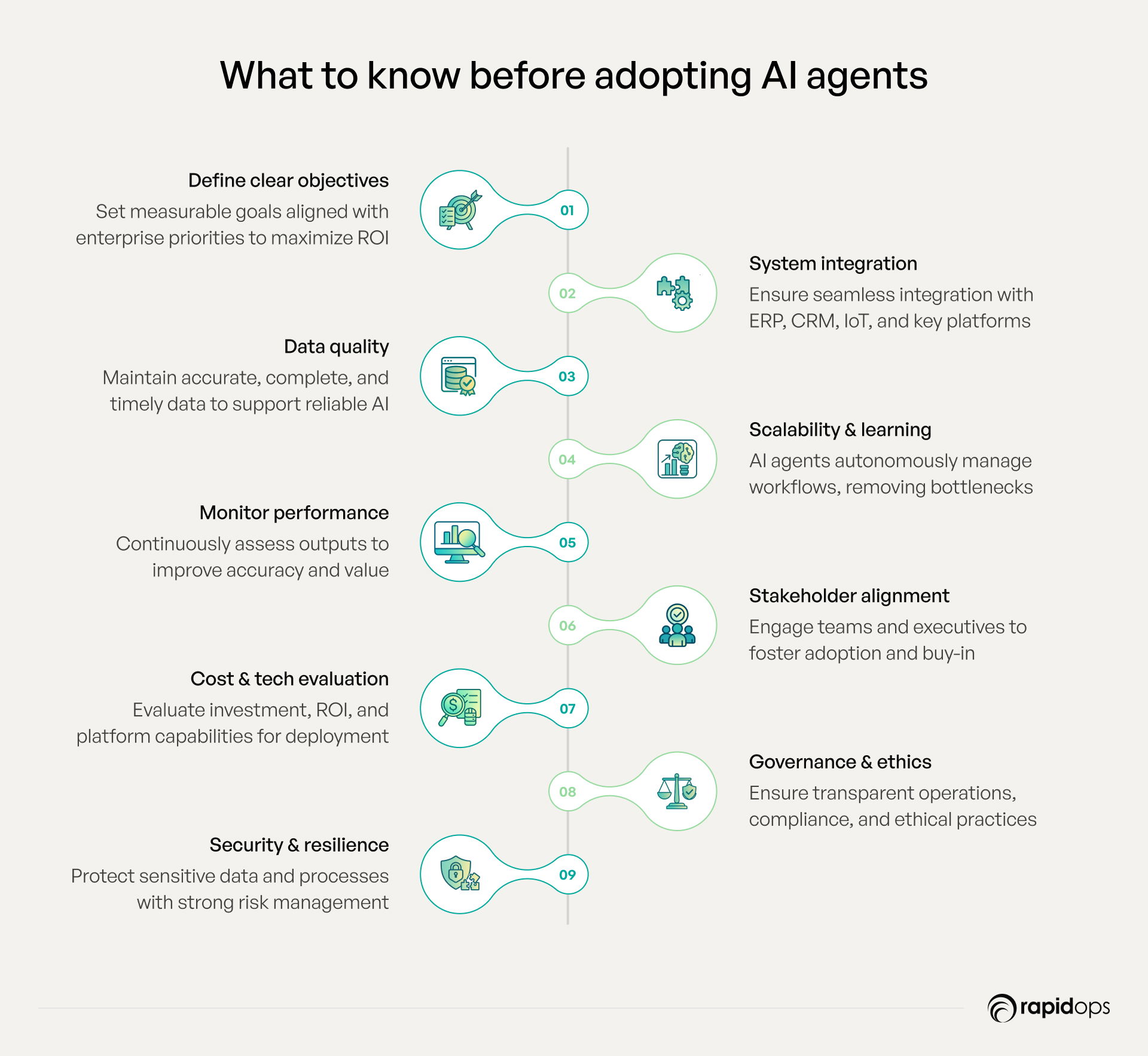
1. Clearly defined objectives and strategic use cases
The effectiveness of AI agents begins with precision in purpose. Leaders must define measurable goals aligned with enterprise priorities, whether optimizing workflows, enhancing customer experiences, or improving resource allocation. Clear objectives create a framework for ROI measurement and ensure AI initiatives contribute to long-term strategic outcomes.
2. Seamless integration with enterprise systems
AI agents deliver maximum value when fully integrated with ERP, CRM, IoT, and other mission-critical systems. Integration enables real-time insights, uninterrupted workflows, and consistent task execution, while eliminating data silos and empowering enterprise-wide AI automation.
3. High-quality data and accessibility
AI performance depends on accurate, complete, and timely data. Enterprises must establish robust governance, ensure secure access, and maintain data integrity to support reliable decision-making, minimize operational risks, and comply with regulatory standards.
Don't think of deploying AI agents without knowing these key factors that drive success & prevent costly mistakes
Download Now
4. Scalability and adaptive intelligence
Enterprise AI must scale across business units, geographies, and processes. Agents capable of learning from historical interactions and adapting to evolving conditions deliver continuous operational efficiency, resilience, and performance improvement.
5. Performance monitoring and continuous improvement
Ongoing evaluation of agent output and alignment with business objectives ensures measurable impact. Continuous refinement enhances accuracy, reliability, and enterprise-wide operational value while enabling agile responses to emerging challenges.
6. Organizational alignment and stakeholder buy-in
Embedding AI into organizational culture is essential. Engaging executives and teams fosters alignment, accountability, and readiness for change, ensuring AI initiatives evolve from pilot projects into enterprise-wide value drivers.
7. Strategic cost-benefit analysis and technology selection
Evaluating investment, expected ROI, and platform capabilities ensures sustainable deployment. Choosing agents and technology aligned with enterprise scale and innovation goals maximizes long-term business value.
8. Governance, oversight, and ethical compliance
Even autonomous agents require structured oversight. Transparent operations, ethical AI practices, and regulatory compliance maintain stakeholder trust, mitigate reputational risks, and support accountable deployment.
9. Security, risk management, and resilience
Agents must operate within secure and resilient environments that protect sensitive data, critical processes, and intellectual property. Comprehensive risk frameworks and contingency planning ensure reliability and enterprise-wide trust.
By addressing these dimensions comprehensively, leaders can deploy AI agents that accelerate time-intensive tasks with unmatched quality, amplify decision-making, drive innovation, and unlock transformative enterprise outcomes, positioning the organization for sustained competitiveness in a rapidly evolving market.
Check how ready you are to deploy AI
agents and find out what you have in
place and what’s still needed!
Assess Now 
Turning AI agents’ capabilities into tangible business performance
You’ve seen what AI agents are, how they operate, and the transformative potential they bring to enterprise workflows, decision-making, and customer interactions. Their true value emerges when these systems are strategically deployed, streamlining operations, accelerating time-intensive tasks, and consistently delivering high-quality outcomes across the organization.
At Rapidops, we leverage extensive hands-on experience helping enterprises harness AI agents to modernize operations and unlock measurable results. From scaling personalized customer interactions to implementing adaptive decision-making systems, our team partners with businesses of all sizes to translate Gen AI strategies into real-world performance improvements that matter.
Curious how AI agents can redefine strategic performance in your enterprise?
Connect with one of our AI agent experts to explore tailored strategies that integrate seamlessly into your operations, transforming AI potential into measurable business value and actionable results.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why are AI agents so popular?
AI agents are popular because they accelerate decision-making, automate repetitive tasks, and optimize operational efficiency. Organizations in retail, manufacturing, and distribution leverage them for predictive inventory management, supply chain optimization, and customer engagement. Their autonomous learning and adaptability allow enterprises to respond rapidly to market changes, reduce operational costs, and gain competitive advantage. By bridging human expertise with computational efficiency, AI agents are emerging as indispensable tools in digital transformation strategies.
What are the cons of AI agents?
Despite their advantages, AI agents pose challenges. Data bias or incomplete training can produce inaccurate outputs, while ethical concerns around accountability, transparency, and unintended consequences must be addressed. Over-reliance may reduce human oversight, and integration with legacy systems can be resource intensive. Enterprises must implement risk management, continuous monitoring, and human-in-the-loop frameworks to mitigate these limitations, ensuring responsible deployment and sustainable value from AI agents without compromising operational integrity or compliance.
Can AI agents be trusted?
Trust in AI agents depends on predictability, transparency, and alignment with organizational ethics. Reliable agents provide consistent outputs, explainable reasoning, and maintain contextual awareness across workflows. Integrating feedback loops and human oversight enhances trust and ensures accountability. Enterprises that combine autonomous AI with governance frameworks can leverage AI agents to make informed decisions, improve operational efficiency, and maintain confidence among stakeholders while mitigating risks associated with fully autonomous operations.
What is a real-life example of an AI agent?
A real-life example of an AI agent is a customer service automation agent used by enterprises. It autonomously manages inquiries across chat, email, and social media, delivering accurate, context-aware responses, resolving routine issues, and escalating complex cases to human specialists. By automating repetitive tasks, it reduces response times, minimizes errors, frees employees for higher-value work, and drives measurable outcomes, improving customer satisfaction, lowering operational costs, increasing efficiency, and creating scalable, resilient enterprise processes. This demonstrates the tangible strategic value of AI agents for businesses.
Are AI agents the next big thing?
AI agents are becoming pivotal in digital transformation, bridging human expertise and machine efficiency. Their autonomous decision-making, adaptability, and ability to integrate with multiple enterprise systems make them central to modern business strategies. Companies using AI agents gain operational agility, cost efficiency, and improved customer engagement. As adoption grows across industries, AI agents are set to redefine workflow automation and strategic decision-making, establishing themselves as a foundational technology for next-generation enterprises.
What are the four main rules for AI agents?
The PART principles Perception, Action, Reasoning, and Trust, guide AI agent operations. Perception enables environmental awareness, Action executes tasks autonomously, Reasoning prioritizes objectives and adapts strategies, and Trust ensures transparency and predictable behavior. Adherence to these rules allows enterprises to deploy AI agents responsibly, achieving operational efficiency, strategic alignment, and ethical AI usage. They provide a framework for scalable, reliable, and accountable autonomous systems.
How do AI agents adapt and learn over time?
AI agents continuously improve through machine learning and feedback loops. They analyze past outcomes, recognize patterns, and adjust strategies to optimize performance. For instance, in customer service, agents refine responses based on resolution success and customer satisfaction data. This iterative learning enhances adaptability, predictive capabilities, and operational foresight, enabling enterprises to scale AI agent usage across dynamic workflows while maintaining high accuracy and efficiency.
How do AI agents enhance customer experience in real-time?
AI agents deliver instant, personalized support by analyzing queries, context, and past interactions. In retail, they guide customers on products and orders; in manufacturing and distribution, they track shipments and resolve routine inquiries. By handling repetitive tasks autonomously, AI agents reduce response times, accelerate issue resolution, and free human teams for complex interactions. Continuous learning ensures smarter, proactive responses, creating seamless experiences that strengthen customer satisfaction, loyalty, and operational efficiency across industries.
Can AI agents be trusted to make autonomous decisions?
Trust in autonomous AI agents is built on predictable performance, explainable reasoning, and ethical governance. Agents must operate within defined parameters, provide auditable decision trails, and incorporate human feedback. Governance frameworks and continuous monitoring ensure accountability and alignment with business objectives. When deployed responsibly, AI agents can autonomously execute complex tasks, delivering operational efficiency, faster decision-making, and strategic insights, while maintaining reliability and minimizing organizational risk.
Can AI agents improve employee onboarding processes?
AI agents streamline employee onboarding by automating repetitive administrative tasks such as document verification, training scheduling, and knowledge distribution. They also provide instant answers to common queries, helping new hires adapt faster. This reduces administrative overhead and ensures consistent, efficient onboarding experience. By integrating AI agents into HR workflows, companies accelerate ramp-up time, improve employee satisfaction, and maintain compliance, while HR teams can focus on strategic initiatives rather than manual processes.
In what ways do AI agents support personalized marketing campaigns?
AI agents drive data-driven marketing by analyzing customer behavior, preferences, and engagement patterns. They enable hyper-personalized campaigns, recommending products, offers, and content tailored to individual users. By predicting purchase intent and segmenting audiences, AI agents increase engagement, conversion rates, and customer lifetime value. Enterprises leveraging these agents can deliver timely, relevant marketing messages at scale, optimizing ROI while maintaining brand consistency and responsiveness across channels.

Rahul Chaudhary
Content Writer
With 5 years of experience in AI, software, and digital transformation, I’m passionate about making complex concepts easy to understand and apply. I create content that speaks to business leaders, offering practical, data-driven solutions that help you tackle real challenges and make informed decisions that drive growth.
What’s Inside
- Demystifying AI agents for business leaders
- What makes an AI agent truly “agentic”
- What is the difference between AI agents, AI assistants, and chatbots?
- Evolution of AI agents in enterprises
- Components of AI agents
- How AI agents work
- Types of AI agents
- What value AI agents are unlocking for businesses
- How AI agents are transforming business operations
- Things to consider when implementing AI agents
- Turning AI agents’ capabilities into tangible business performance

Let’s build the next big thing!
Share your ideas and vision with us to explore your digital opportunities
Similar Stories
- AI
- 4 Mins
- September 2022

- AI
- 9 Mins
- January 2023


Receive articles like this in your mailbox
Sign up to get weekly insights & inspiration in your inbox.

