Are your software initiatives delivering real business impact or just costing time and money? How often do projects miss deadlines, deliver misaligned features, or fail to integrate smoothly with existing processes? These challenges don’t just frustrate teams; they affect revenue, customer experience, and your competitive edge. And whether you rely on internal teams or external partners, the stakes are the same: every decision matters.
In 2025, software is more than a solution; it’s a strategic driver of business success. Yet many organizations struggle to ensure solutions truly meet their needs. Projects that lack clear alignment with business goals or disciplined oversight risk turning potential opportunities into costly delays and wasted investment.
The most successful executives approach software development as a strategic capability, not just a technical task. They embed structured, outcome-focused practices across planning, vendor collaboration, testing, and delivery. The result? Every initiative, internal or outsourced, delivers measurable value, speeds time-to-market, and strengthens long-term performance.
In this article, we reveal ten best practices for modern software development in 2025, designed to help you manage risks, guide projects effectively, and transform every software initiative into a predictable engine of innovation, efficiency, and growth.
Why 2025 marks a new era in software development
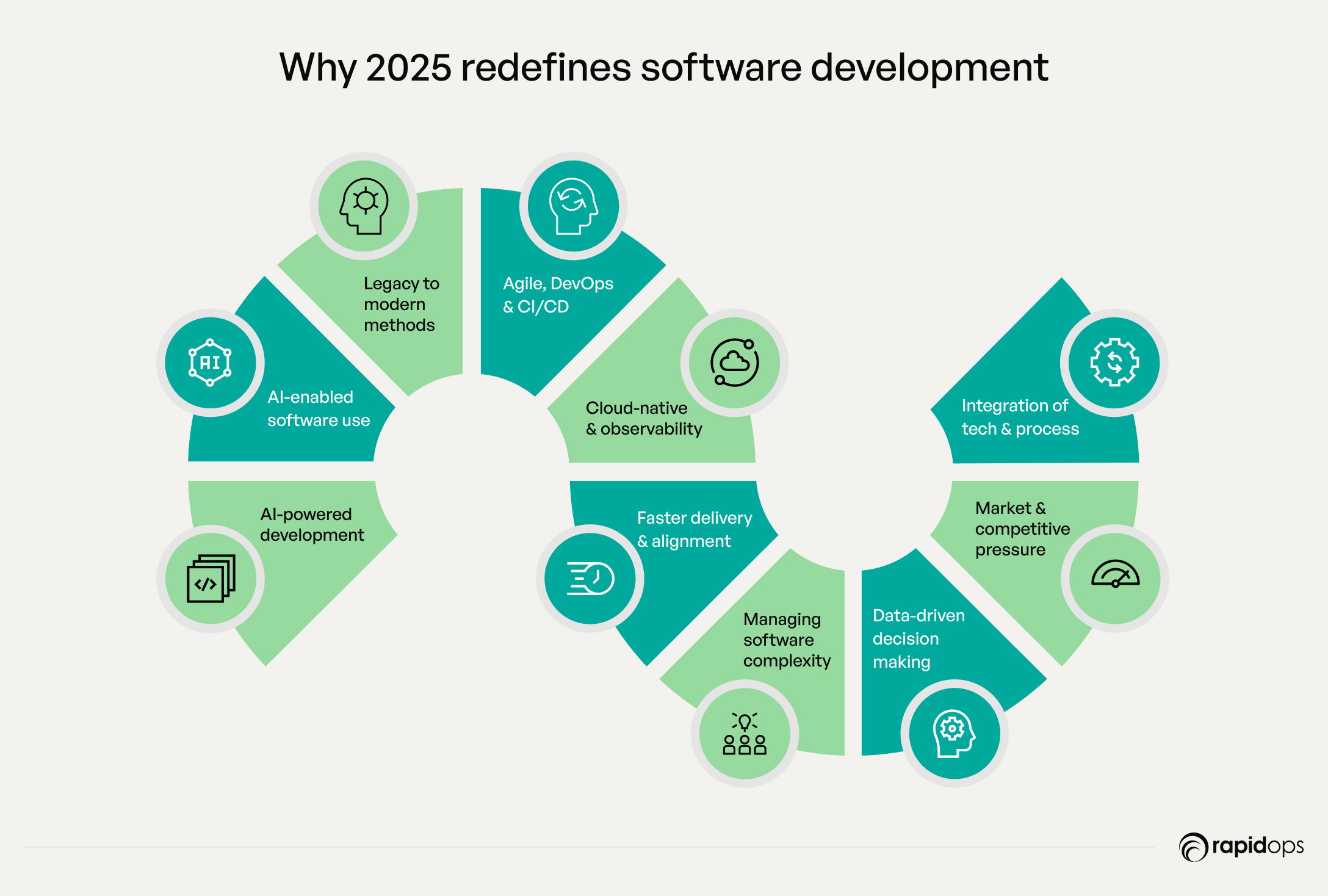
2025 ushers in a new era of software development, where success depends on rethinking how software is planned, built, and delivered. Companies that adapt to projects can turn into growth engines and sustain a competitive edge in an increasingly complex landscape.
AI-powered development
As we enter 2025, software development is entering a new era defined by intelligence, automation, and predictive capabilities. AI-powered development is at the forefront of this transformation, enabling teams to anticipate code defects, automate testing, and accelerate deployment cycles like never before. By integrating AI in software development, businesses can reduce technical debt, improve software quality, and make more informed decisions about resource allocation and risk management. With emerging AI tools and frameworks becoming mainstream in 2025, organizations now have the opportunity to build more adaptive, resilient, and future-ready software than ever before.
AI-enabled software as a must-have
In 2025, AI-enabled software is a strategic imperative, driving both competitiveness and efficiency across organizations. By leveraging AI, leaders can speed up time-to-market, anticipate business trends with predictive insights, and maximize ROI on every project. Integrated AI-driven testing ensures software is reliable, reduces operational risks, and scales seamlessly as business demands grow. For executives steering internal teams or external partners, adopting AI in development isn’t just a technological choice, it’s a way to unlock innovation, optimize resources, and make every software initiative a measurable driver of business value.
From legacy practices to modern approaches
In 2025, software development is entering a new era defined by speed, agility, and strategic business impact. Many organizations are still moving away from legacy waterfall methods, which often cause delayed delivery, fragmented code, and unmanaged technical debt.
Modern approaches, including agile methodologies, code reviews, continuous integration, and version control, create structured, collaborative, and outcome-driven development environments that align technology with business objectives. Transitioning effectively requires executive sponsorship, clear strategic alignment, and a focus on measurable results, ensuring software initiatives not only deliver on time but also drive innovation, efficiency, and long-term competitive advantage.
Standardization of agile, DevOps, and CI/CD
Agile, DevOps, and CI/CD pipelines have become standardized practices in high-performing software teams. Agile methodology ensures iterative development and stakeholder alignment, while DevOps promotes collaboration between development and operations teams. Continuous integration and automated deployment streamline the delivery process, ensuring that software quality and functionality are validated continuously. Adopting a structured software development methodology that incorporates these practices allows executives to achieve predictable delivery, higher efficiency, and measurable outcomes.
Cloud-native architectures and observability
Modern software is increasingly built on cloud-native architectures, enabling scalability, flexibility, and resilience. Observability tools provide real-time insights into performance, errors, and system health. Integrating these with software architecture best practices ensures well-structured, modular systems that simplify maintenance and accelerate new feature development. This approach also improves code readability, deployment efficiency, and operational reliability.
Faster delivery, agility, and business alignment
High-performing teams in 2025 deliver software faster without sacrificing quality. Streamlined development processes, combined with automated testing and deployment, improve agility while ensuring alignment with business strategy. Executives can measure impact through KPIs like deployment frequency, production stability, and development time efficiency. Modern software development practices focus on bridging the gap between technical execution and strategic business outcomes.
Managing increasing software complexity
As software systems grow in scope and interconnectivity, complexity management is critical. Practices like modular software design, coding standards, code organization, and regular code reviews help manage complexity and reduce human error. Tracking dependencies and maintaining consistent code structure ensures maintainable systems that scale effectively while minimizing technical debt.
Data-driven decision making in development
In 2025, software development is increasingly guided by data at every stage. Teams leverage metrics from CI/CD pipelines, automated testing, and code quality analysis to inform task prioritization, resource allocation, and risk management. Dashboards tracking unit test coverage, integration tests, and performance indicators provide actionable insights for executives and development leads, enabling decisions that optimize speed, quality, and business outcomes. Organizations that adopt modern strategies data-driven decision-making can predict issues, refine processes, and ensure that development aligns closely with strategic goals, turning data into a competitive advantage.
Market pressures and competitive imperatives
Businesses in 2025 face intense market pressures requiring rapid software innovation. Organizations that fail to adopt modern software development practices risk falling behind competitors. Efficient, agile, and automated development processes enable rapid feature delivery, optimized business logic, and high-quality software that support strategic goals.
Integration of technology, process, and strategy
The new era of software development is defined by the integration of technology, process, and business strategy. Executives must ensure that AI-powered development, cloud-native architectures, CI/CD pipelines, and agile practices are applied cohesively. When executed effectively, software development best practices deliver measurable outcomes: faster delivery, reduced risk, higher software quality, and strategic alignment.
2025 marks a turning point in software development. Organizations that adopt AI-driven workflows, standardized agile and DevOps practices, cloud-native architectures, and disciplined software development practices will outperform competitors.
By integrating technology, process, and strategy, executives can ensure that software initiatives, whether internally or outsourced, become reliable drivers of innovation, efficiency, and long-term business success.
10 software development best practices driving strategic impact
In a world where speed and innovation determine success, software initiatives must deliver more than functionality. Organizations that embed structured practices across every development phase transform projects into engines of measurable value and lasting competitive advantage.
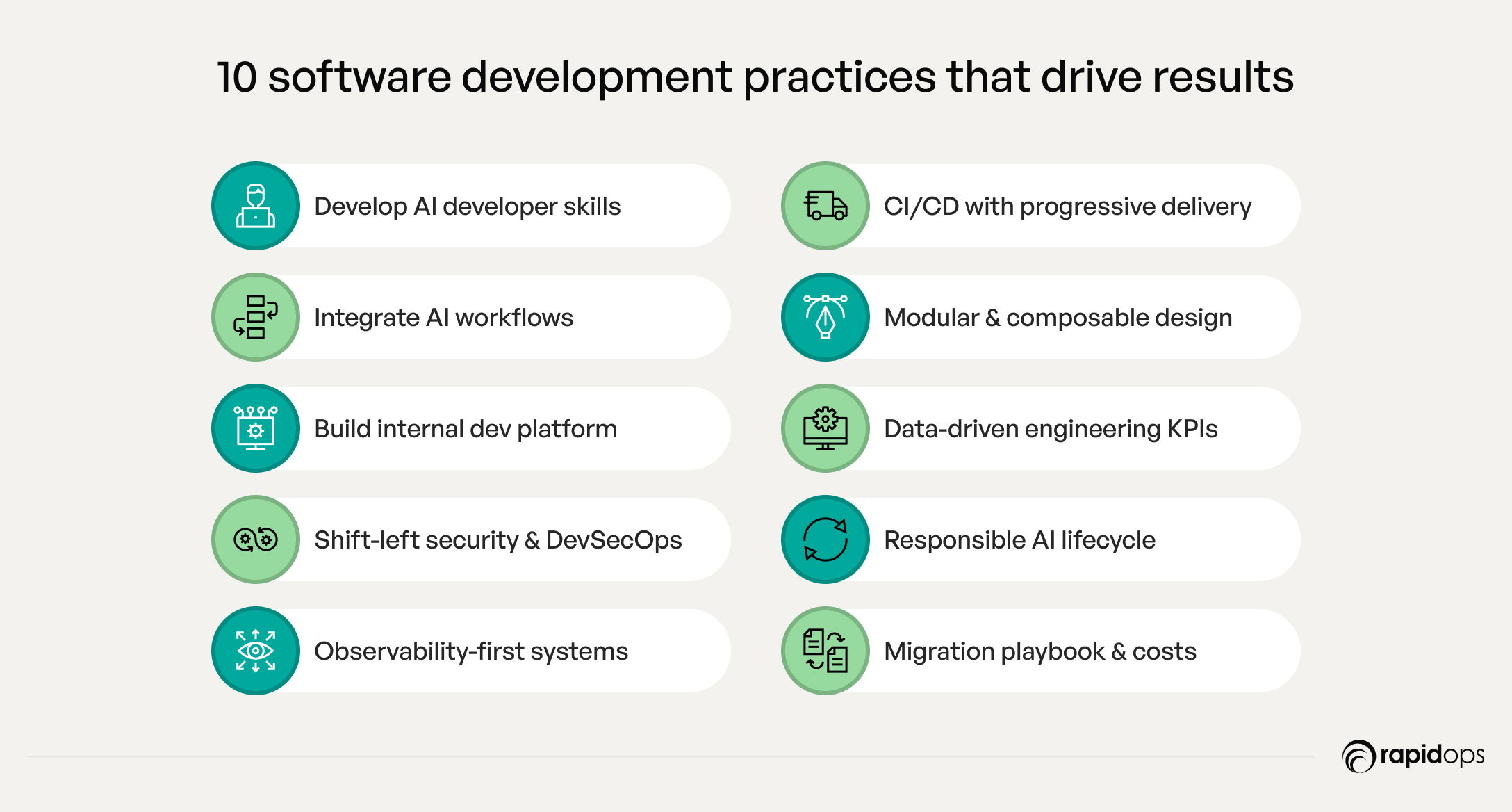
1. Develop AI-enabled developer skills
In 2025, achieving high-quality software depends as much on your developers' skills as on the technologies and tools you use. For executives managing software initiatives, whether built internally or through external vendors, the critical question is whether teams have the capability to leverage AI-driven insights effectively, align with your software development best practices, and produce measurable business outcomes.
Teams skilled in AI-assisted development accelerate delivery, reduce technical debt, and ensure consistent adherence to modern software development practices. When engaging external vendors, evaluating their AI proficiency and ability to adopt tools and processes aligned with your objectives is essential to avoid delays and costly mistakes.
Core capabilities
- AI literacy & fluency: Ensure internal or vendor teams can interpret AI-driven code recommendations and predictive insights safely.
- Practical AI application: Confirm that AI is integrated into testing, deployment pipelines, and automated code quality checks.
- Continuous learning culture: Assess whether teams follow ongoing training programs, peer mentoring, and knowledge sharing to maintain skill relevance.
- Cross-functional collaboration: Developers should work closely with product, operations, and security teams to align software initiatives with broader business goals.
Implementation approach
- Skills gap assessment: Identify gaps in internal teams or vendors to ensure AI capabilities meet your strategic requirements.
- Performance monitoring: Track metrics such as deployment speed, defect reduction, and code quality to ensure outcomes align with expectations.
- Vendor evaluation: Require proof of AI proficiency and real-world application when selecting external partners.
Investing in AI-enabled developer skills ensures your software initiatives, internal or outsourced, deliver high-quality software faster, reduce operational risks, and provide executives with confidence that AI adoption translates into measurable business value
2. Integrate AI-assisted workflows with governance
AI-assisted workflows are no longer optional; they are now central to maintaining software quality, efficiency, and compliance. For executives, the key is ensuring that both internal teams and external partners follow governed workflows that accelerate delivery while minimizing risk. AI-powered development helps reduce human error, optimize the software development process, and improve outcomes. Without proper governance, AI adoption can introduce inconsistencies or compliance gaps, particularly when working with external vendors.
Core capabilities
- Intelligent coding assistance: Confirm teams use AI for code suggestions, pattern recognition, and automated testing to reduce errors.
- AI-powered testing & validation: Ensure CI/CD pipelines incorporate AI to detect defects early, improving code quality and reliability.
- Governance framework: Policies for code reviews, logging, and compliance audits ensure both internal and vendor teams adhere to organizational standards.
Implementation approach
- Pilot low-risk workflows: Start small to measure AI impact on software development practices and overall delivery speed.
- Track metrics: Monitor deployment velocity, bug reduction, and adherence to standards.
- Scale with oversight: Expand AI workflows while enforcing structured governance to maintain quality, accountability, and risk management.
Properly governed AI-assisted workflows enable executives to ensure that software initiatives, whether internal or outsourced, deliver predictable, high-quality software that aligns with strategic business goals.
3. Build an internal developer platform (IDP) / Self-service layer
Operational friction remains one of the biggest roadblocks to efficiency and innovation in modern software development. An Internal Developer Platform (IDP) centralizes tools, workflows, and reusable templates, allowing internal teams and external partners to self-serve development processes, manage deployment pipelines, and consistently follow best practices.
IDPs reduce errors, accelerate delivery, and ensure standardized software development practices. For organizations developing web applications, adopting a structured web application development process for businesses ensures that both internal and outsourced teams adhere to code review standards, automated testing protocols, and governance guidelines. This alignment guarantees outcomes that meet business objectives and maintain high quality across all projects.
Core capabilities
- Infrastructure abstraction: Provide seamless access to environments, resources, and deployment configurations without bottlenecks.
- Reusable templates & pipelines: Standardize CI/CD workflows, automated testing, and deployment scripts for predictable execution.
- Metrics & access control: Track adoption, workflow efficiency, and software quality while maintaining oversight.
Implementation approach
- Pilot and iterate: Start with a single team or vendor to validate workflows and refine features.
- Embed KPIs: Measure deployment velocity, defect rates, and compliance with standards.
- Extend to external vendors: Ensure all outsourced teams follow the IDP to maintain alignment with internal software development best practices.
A well-implemented IDP empowers teams, reduces operational friction, and provides executives with a strategic mechanism to ensure scalable, predictable, and high-quality software delivery, whether for internal projects or outsourced web applications.
4. Shift-left security & DevSecOps
Security is no longer a final step; it’s a strategic imperative. Embedding security early in the software development process transforms risk management from reactive to proactive. Addressing vulnerabilities during design and coding reduces remediation costs by 15–30x compared to fixes in production.
For executives working with external vendors, shift-left security ensures projects are resilient, compliant, and aligned with organizational risk tolerance while supporting high-quality software delivery.
Core capabilities
- Automated code and dependency analysis: Identify vulnerabilities in both internal and outsourced source code at the earliest stages.
- Policy-as-Code: Embed security policies directly into CI/CD pipelines.
- Automated deployment gates: Prevent non-compliant or high-risk code from progressing.
- Proactive risk management: Continuously monitor secrets, dependencies, and configuration risks.
Implementation approach
- Integrate security checks early, starting with high-impact modules.
- Expand practices across internal teams and external development partners, creating feedback loops for continuous improvement.
- Track software quality, defect reduction, and compliance adherence to ensure predictable outcomes.
Shift-left security paired with DevSecOps reduces operational risk, strengthens compliance, and ensures software initiatives, internal or outsourced, deliver high-quality software consistently.
5. Observability-first architecture
Modern software is only as valuable as its reliability. Adopting an observability-first approach transforms opaque systems into measurable, transparent systems, directly supporting enterprise modernization initiatives by providing visibility across processes, infrastructure, and applications. This approach enables executives to make informed decisions, anticipate risks, and maintain confidence in software outcomes. For organizations working with external vendors, observability ensures alignment, accountability, and transparency across the entire software development lifecycle.
Core capabilities
- Comprehensive monitoring: Metrics, traces, and logs provide visibility into software quality and system health.
- Intelligent alerting: Alerts tied to business and technical KPIs enable rapid response.
- System health dashboards: Real-time insights into error rates, performance, and SLOs.
- Dependency awareness: Detect bottlenecks or potential failure points early.
Implementation approach
- Instrument key workflows, define KPIs aligned with business objectives, and establish dashboards.
- Expand coverage across internal and external development teams to ensure predictable software development outcomes.
- Continuously measure deployment processes, code quality, and technical debt to maintain operational resilience.
An observability-first architecture provides executives with actionable insights, accelerates delivery, and supports high-performing software development practices with measurable business value.
6. CI/CD with progressive delivery
Implementing CI/CD with progressive delivery transforms software deployment into a predictable, rapid, and low-risk process. It enables high-performing teams to release features more frequently while minimizing failure rates, ensuring that updates reach users efficiently without disrupting business operations. Organizations that leverage progressive delivery experience faster feedback loops and improved collaboration among development, QA, and operations teams.
Core capabilities
- Automated pipelines: Standardized workflows automate build, test, and deployment processes, reducing manual errors and increasing efficiency.
- Feature flags and staged rollouts: Control exposure of new features, enabling safe experimentation and incremental releases.
- Canary and blue-green deployments: Gradually release updates to a subset of users to detect issues early without impacting all customers.
- Rollback strategies: Quickly revert changes when incidents occur, ensuring continuity and reliability.
Implementation approach
Build CI/CD pipelines that integrate automated testing, progressive delivery, and deployment monitoring. Start with non-critical applications to validate processes, then scale across internal and external development teams. Continuously measure performance, refine workflows, and expand staged deployment strategies to align with organizational priorities.
CI/CD with progressive delivery is not merely a technical enhancement; it is a strategic enabler. Executives can ensure predictable releases, reduce operational risk, and maintain business agility. By embedding progressive delivery into development practices, organizations accelerate innovation while safeguarding reliability, quality, and customer trust.
7. Modular & composable architecture
A modular, composable architecture enables companies to scale software initiatives without increasing complexity. By allowing independent development, deployment, and maintenance of components, executives can ensure that software delivered by external vendors meets software development best practices and aligns with business goals.
Core capabilities
- Microservices & domain-driven design: Loosely coupled services aligned with business domains.
- Plugin & modular components: Reusable building blocks to accelerate feature delivery.
- API versioning & integration: Maintain compatibility across internal and external systems.
- Service mesh & orchestration: Enhance observability, security, and resilience across modules.
Implementation approach
- Define module boundaries, start with critical systems, and monitor component interactions.
- Apply modular principles consistently across internal teams and external partners.
- Track technical debt, code organization, and deployment processes to ensure maintainability and scalability.
Modular architecture empowers executives to innovate rapidly, minimize human error, and deliver high-quality software consistently, regardless of whether development is internal or outsourced.
8. Data-driven engineering metrics & KPIs
Implementing data-driven engineering metrics transforms the software development process into an evidence-based, strategic approach. Organizations that track performance across software development projects, development teams, and software development practices gain transparency into system reliability, software quality, and operational efficiency.
Metrics provide executives with actionable insights to identify bottlenecks, reduce technical debt, and optimize resource allocation across both internal teams and external partners. Teams leveraging DORA metrics, unit tests, and integration tests can recover from incidents faster, maintain high code quality, and continuously improve software development processes.
Core capabilities
- DORA metrics: Track deployment frequency, change lead time, MTTR, and change failure rate to measure software reliability.
- Reliability and security KPIs: Monitor uptime, error rates, and compliance adherence to ensure high-quality software.
- Productivity and efficiency metrics: Measure throughput, cycle times, and work-in-progress to optimize the development process and reduce development time.
- Dashboards and visual reporting: Provide real-time visibility into software architecture, code quality, and system performance to support informed decision-making.
Implementation approach
Define KPIs aligned with business objectives. Instrument CI/CD pipelines, version control systems, and testing frameworks to capture relevant data. Establish dashboards for continuous monitoring, regularly review metrics, and iterate workflows. Expand visibility across software developers, development teams, and external partners to maintain accountability and consistency.
Data-driven metrics enable executives to bridge the gap between development practices and business objectives, ensuring predictable outcomes, high-quality software, and measurable strategic value.
9. Responsible AI & model lifecycle management
Responsible AI ensures AI-enabled software is developed, deployed, and maintained securely, ethically, and in compliance with software development standards. Proper governance reduces operational, legal, and reputational risks while supporting trustworthy software outcomes. Executives overseeing AI initiatives, whether built by internal teams or external partners, can ensure alignment with business strategy and measurable results.
Core capabilities
- Model versioning and governance: Track AI model versions, updates, and changes to maintain software development standards and reproducibility.
- Prompt provenance and auditing: Maintain clear records of AI inputs, outputs, and decisions to enable accountability and enforce software development practices.
- Validation and testing: Continuous testing for bias, accuracy, and reliability ensures high-quality software.
- Compliance policies: Integrate regulatory and ethical standards into the AI software development process.
Implementation approach
Establish an AI model registry and governance framework. Define testing, unit testing, and validation procedures to monitor model performance. Audit usage regularly and enforce compliance checkpoints across development teams and external software developers. Expand adoption gradually to ensure both internal and external teams follow software engineering practices.
Responsible AI is a strategic capability that allows executives to maintain software quality, mitigate risk, and drive measurable business value across all software development projects.
10. Migration playbook & cost allocation strategy
A structured migration playbook with a cost-allocation strategy ensures a smooth transition to modernization, cloud adoption, or tooling changes while maintaining high-quality software delivery. Proper planning reduces budget overruns, mitigates operational risk, and supports continuity across internal teams and external partners.
Core capabilities
- Phased migration planning: Break large migrations into manageable stages to maintain business continuity.
- Pilot teams and testing: Validate workflows with unit tests, integration tests, and quality assurance testing before full rollout.
- Cost tracking and allocation: Assign budgets, track expenditures across software development projects, and prevent overruns.
- Rollback and contingency strategies: Ensure operational stability in case of unexpected challenges.
- Stakeholder communication: Keep executives, development teams, and external partners aligned on progress and expectations.
Implementation approach
Develop a detailed roadmap identifying dependencies, risks, and priorities. Deploy pilot teams to test processes, monitor outcomes, and refine strategies. Use CI/CD pipelines and automated testing to ensure safe deployment. Expand in phases across internal teams and external software developers. For organizations aiming to accelerate these efforts, leveraging the strategies outlined in speed up code migration with gen-ai can help optimize migration timelines and reduce operational bottlenecks.
A disciplined migration and cost-allocation strategy enables executives to manage software development projects predictably, maintain software quality, and maximize ROI. This approach ensures modernization initiatives drive innovation, operational resilience, and long-term business value.
Tools & vendor landscape
Modern software development in 2025 requires more than just capable teams—it depends on a strategic ecosystem of tools, platforms, and practices that ensure high-quality software, predictable delivery, and measurable business outcomes. For organizations commissioning software from external partners, selecting the right tools is critical to avoid technical debt, operational delays, and misaligned business logic.
Tool categories & strategic value
CI/CD platforms & deployment process: standardized pipelines automate testing, continuous integration, and progressive deployment, reducing human error and accelerating delivery. Executives should ensure external teams adhere to software development standards, coding conventions, and input validation, which maintain consistent code quality across releases.
Internal developer platforms (IDPs)
Self-service platforms provide access to reusable templates, unit tests, and CI/CD workflows, enabling development teams to maintain well-structured, well-organized code and conduct regular code reviews. External developers can leverage IDPs to align with your software development process while reducing time spent on repetitive tasks.
Observability & monitoring tools
Comprehensive dashboards track software quality, performance optimization, and the health of the production environment, providing executives with actionable insights to manage risk and ensure high-quality software products. Observability also supports integration tests, code comments, and knowledge sharing, ensuring development practices remain transparent across internal and external teams.
Security & DevSecOps tools
Incorporating shift-left security, static code analysis, secure coding practices, and automated testing helps protect software from vulnerabilities and enforce compliance. Executives commissioning software externally should evaluate vendor adherence to security considerations, coding standards, and quality assurance testing.
AI-assisted development tools
Modern platforms enable intelligent code suggestions, automated unit tests, and predictive issue detection, helping teams develop software efficiently, maintain code readability, and reduce technical debt. Executives can assess how vendors integrate ai into development practices to optimize development time and improve software architecture.
Metrics, dashboards, and analytics platforms
Real-time reporting on deployment, continuous integration, software development projects, and software quality provides transparency and accountability. Monitoring development teams, the development process, and source code quality ensures measurable outcomes and supports performance optimization.
Strengths, trade-offs & vendor evaluation
Every tool category delivers unique benefits, but differences in integration, scalability, and usability can impact software engineering practices. Executives should evaluate:
- Vendor adherence to software development best practices
- Consistency in code formatting, coding conventions, and version control
- Ability to maintain unit tests, integration tests, and CI/CD pipelines
- Support for new features, modular architecture, and design principles
Pairing complementary tools, such as AI-assisted development, with CI/CD pipelines and observability dashboards enhances software development practices and ensures high-quality software outcomes for both internal and external teams.
Cost & adoption considerations
Tools range from freemium to enterprise-grade. Investment decisions should focus on roi, long-term scalability, software product reliability, and the effort required to train internal teams and external partners. Phased rollout, comprehensive onboarding, and ongoing knowledge sharing ensure smooth adoption while maintaining software quality and adherence to software development standards.
Emerging trends
Low-code/no-code platforms, automated governance, and AI-driven workflows are redefining modern software development. Executives leveraging these technologies with external vendors can reduce development time, human error, and operational risks while improving code readability, structure, and quality across software development projects.
By strategically evaluating tools and aligning them with software engineering practices, development teams, and software development processes, executives can ensure every software initiative, internal or outsourced, delivers high-quality software, predictable outcomes, and measurable business value.
Critical challenges in today’s software development landscape
In 2025, software development is a strategic driver of growth, innovation, and competitive advantage, but organizations face a complex landscape of interconnected challenges that can slow delivery, elevate risk, and impact long-term business outcomes.
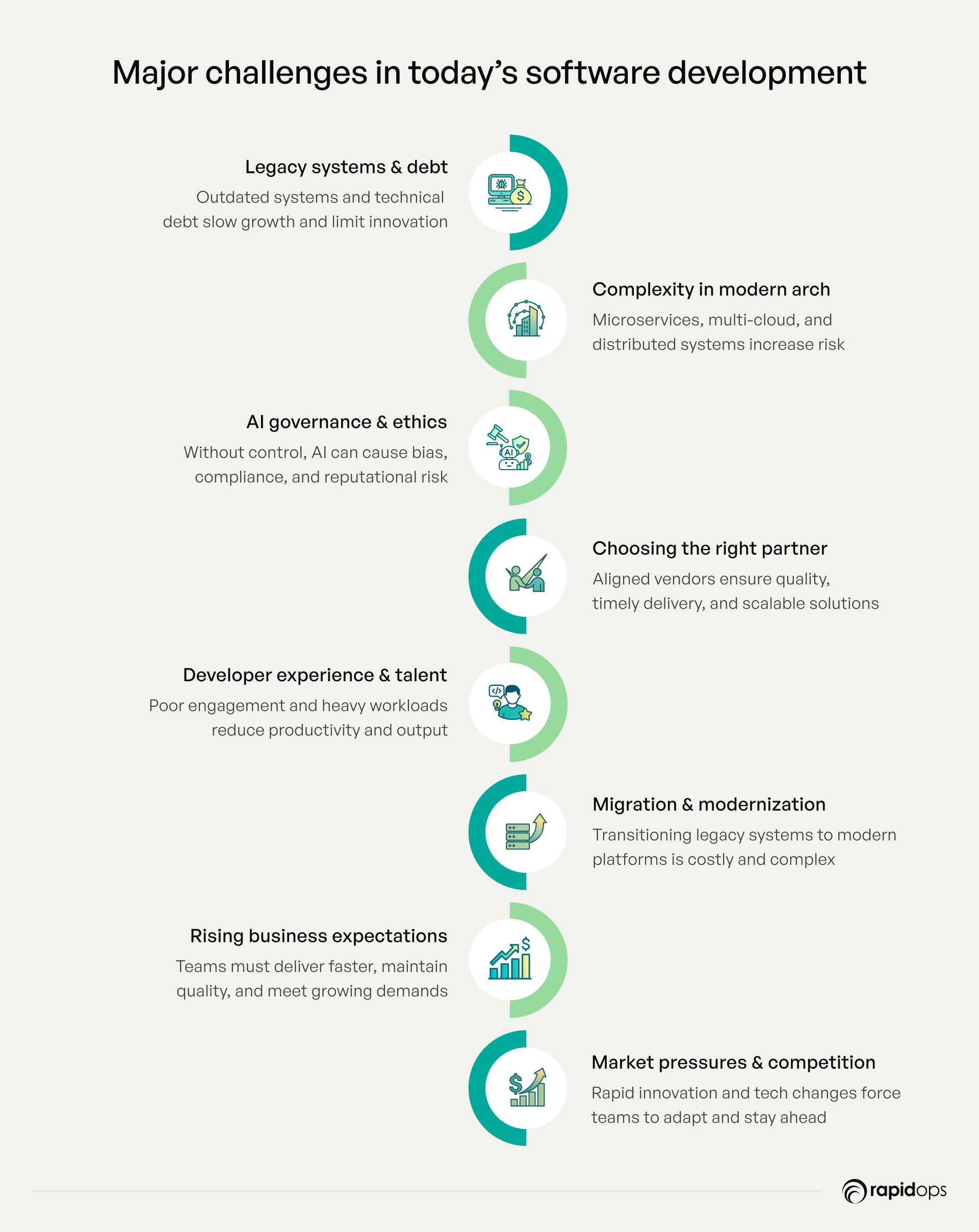
Legacy processes and technical debt
Outdated systems and accumulated technical debt act as hidden bottlenecks, increasing maintenance costs, slowing innovation, and limiting adoption of emerging technologies. Executives must recognize these constraints as a direct risk to scalability, operational efficiency, and strategic agility.
Complexity of modern architectures
Microservices, multi-cloud deployments, and distributed systems provide flexibility but introduce operational complexity. Interdependencies, failure points, and visibility challenges can disrupt delivery, increase costs, and require advanced governance, underscoring the need for strategic architectural oversight.
AI governance and responsible adoption
AI adoption carries ethical, regulatory, and operational risks. Without robust governance, bias, non-compliance, or reputational damage can compromise business outcomes. Forward-looking executives must ensure AI initiatives are accountable, safe, and strategically aligned.
Finding the right software development partner
For organizations without in-house capabilities or seeking advanced software solutions, choosing the right external partner is critical. Misaligned partners can cause delays, cost overruns, or suboptimal quality. Executives must evaluate vendors for technical expertise, delivery reliability, strategic alignment, and ability to scale with business objectives.
Developer experience and talent retention
Skilled developers are the backbone of innovation. Poor experience, high workloads, or limited growth opportunities lead to attrition, lower productivity, and delayed project delivery, directly influencing strategic initiatives and time-to-market.
Migration and modernization hurdles
Transitioning legacy systems to modern architectures or cloud-native platforms is complex and resource-intensive. Delays, integration challenges, or operational disruptions can stall innovation and weaken competitive positioning.
Escalating business expectations
Organizations face growing demands for faster delivery, higher quality, and continuous innovation. Teams must balance speed with resilience, as misalignment can compromise strategic goals.
Competitive pressures and market speed
Rapid market evolution and emerging technologies force organizations to innovate and deliver at pace. Failure to adapt quickly risks lost opportunities, reduced market share, and diminished relevance.
These challenges are rarely isolated; legacy constraints amplify complexity, governance lapses increase security risk, and talent shortages intensify delays. Recognizing their interconnections is essential for developing strategies that sustain growth and maintain competitive advantages.
Building resilient software for the future
Creating software that lasts goes beyond writing code; it’s about delivering solutions that adapt, scale, and provide real value to your business and users. Many projects face delays, features fall short of expectations, or new technologies fail to generate the anticipated impact.
The difference between struggle and success lies in adopting best practices, aligning strategy with execution, and fostering a culture of collaboration, experimentation, and continuous improvement.
At Rapidops, we implement industry-leading software development best practices that drive measurable results. Beyond following standards, we set benchmarks and innovate new practices that enhance efficiency, reliability, and business impact. Through agile workflows, AI-enabled tools, secure architectures, and collaborative cross-functional approaches, we ensure every project delivers strategic value, accelerates growth, and elevates user experience.
Planning to build a new enterprise software or curious how to turn your vision into a high-performing, modern solution? Schedule a session with our software development experts today and discover how we can build resilient, scalable, and innovation-driven software for your business, empowering your users and positioning your organization to thrive for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
What defines modern software development in 2025 and why is it important?
Modern software development in 2025 is defined by the integration of agile methodologies, DevOps practices, cloud-native architectures, and AI-driven automation. It emphasizes speed, flexibility, scalability, and collaboration across cross-functional teams. Unlike traditional approaches, modern development prioritizes continuous delivery, iterative improvements, and a strong focus on user experience. Its importance lies in enabling organizations to quickly respond to market demands, reduce time-to-market, and maintain a competitive edge by delivering high-quality software that aligns with business objectives.
How do agile and DevOps methodologies drive efficiency and innovation?
Agile promotes iterative development, rapid prototyping, and constant feedback loops, ensuring that software aligns closely with user needs. DevOps bridges development and operations, emphasizing automation, continuous integration, and continuous delivery. Together, these methodologies reduce bottlenecks, accelerate release cycles, improve collaboration, and minimize operational risks. They foster a culture of innovation by allowing teams to experiment safely, respond to feedback quickly, and continuously optimize both processes and products.
Why is automated testing critical for high-performing software teams?
Automated testing ensures that software changes are verified consistently and reliably, reducing human error and accelerating release cycles. It allows teams to execute repetitive test cases at scale, identify bugs early, and maintain high quality across complex applications. In high-performing teams, automated testing not only improves code reliability but also enables continuous integration and deployment, freeing developers to focus on innovation rather than manual quality checks.
What metrics should businesses track to measure software development success?
Key metrics include deployment frequency, lead time for changes, mean time to recovery (MTTR), defect density, code coverage, and customer satisfaction. Tracking these metrics provides insights into development efficiency, code quality, operational reliability, and the overall impact on business outcomes. For example, faster deployment frequency paired with low defect density indicates an agile and effective development process, while MTTR helps measure resilience and operational readiness.
How can AI and machine learning enhance software development processes?
AI and machine learning can automate repetitive tasks, such as code generation, bug detection, and testing, reducing time and effort for developers. Predictive analytics can anticipate system failures, optimize resource allocation, and enhance decision-making. AI-powered tools also improve code quality through automated review, identify patterns in user behavior for smarter product design, and accelerate software delivery. Ultimately, AI integration enables faster innovation, fewer errors, and more strategic use of human talent.
What strategies help teams maintain software quality and minimize bugs in modern development?
Maintaining quality requires a multi-layered approach: implementing automated testing and continuous integration pipelines, conducting peer code reviews, and enforcing coding standards. Incorporating test-driven development (TDD) and behavior-driven development (BDD) ensures that functionality aligns with requirements from the outset. Regular monitoring, early defect detection, and robust feedback loops empower teams to address issues before they escalate, resulting in stable, reliable, and maintainable software.
How does modern software development directly impact business growth and ROI?
Modern software development accelerates time-to-market, enhances product quality, and improves customer satisfaction, all of which drive revenue growth. Efficient development practices reduce operational costs, minimize downtime, and optimize resource utilization. Agile and DevOps frameworks enable faster adaptation to market changes, ensuring that products remain competitive and aligned with user needs. By delivering high-quality software rapidly and predictably, businesses achieve measurable ROI and sustain long-term strategic advantage.

Rahul Chaudhary
Content Writer
With 5 years of experience in AI, software, and digital transformation, I’m passionate about making complex concepts easy to understand and apply. I create content that speaks to business leaders, offering practical, data-driven solutions that help you tackle real challenges and make informed decisions that drive growth.

Let’s build the next big thing!
Share your ideas and vision with us to explore your digital opportunities
Similar Stories
- Strategy
- undefined Mins
- February 2017

- AI
- 4 Mins
- September 2022


Receive articles like this in your mailbox
Sign up to get weekly insights & inspiration in your inbox.

