Every day, businesses operate in environments filled with motion, complexity, and high stakes: products moving at speed, customers interacting across multiple channels, machines cycling through thousands of operations, and frontline teams managing tasks where even small errors can cascade into major consequences. Traditional systems and human oversight alone often fall short of providing the clarity needed to navigate this complexity.
Computer vision changes the game by enabling AI to “see” the physical world like humans do, interpreting visual data in real time to extract meaningful insights. By transforming raw digital images, video streams, and visual signals into structured, actionable intelligence, computer vision allows organizations to detect emerging defects on production lines, monitor inventory accuracy, track customer behavior, and identify subtle compliance lapses, before they impact business outcomes.
The value goes far beyond operational efficiency. Businesses can enhance customer experiences, ensure consistent product quality, prevent costly risks, optimize resource allocation, and make faster, smarter decisions across all functions. From manufacturing floors to retail spaces and service touchpoints, computer vision integrates with AI to turn visual intelligence into measurable business impact.
In short, computer vision equips leaders with the eyes to see the unseen, enabling them to act with speed, precision, and confidence, delivering measurable improvements in operational efficiency, customer satisfaction, quality control, risk mitigation, and overall business performance.
Understanding computer vision solutions for business
A computer vision solution is a sophisticated technology that enables businesses to analyze and interpret visual data, such as images, video streams, and live camera feeds, at scale. Unlike traditional analytics, which rely on structured numerical data, computer vision uses artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and deep learning algorithms to extract actionable insights from visual inputs, enabling organizations to make faster, more precise decisions.
In practical terms, computer vision transforms visual elements into meaningful information. From monitoring production processes for quality control to tracking inventory accuracy to understanding customer behavior in retail spaces, these solutions extend the power of AI beyond data spreadsheets, giving businesses a lens into the physical world with human-like perception but far greater speed and scale.
A typical computer vision solution combines image-capture hardware, such as cameras or sensors, with computer vision algorithms and AI models running on robust platforms, creating an integrated system that efficiently processes visual data.
These systems can perform tasks like object detection, image recognition, pose estimation, facial recognition, and visual inspection. By doing so, they help enterprises detect anomalies, monitor operations in real time, and extract insights from huge volumes of visual data that would be impossible to process manually.
The adoption of computer vision solutions is growing rapidly. The global computer vision market is projected to reach $34.3 billion by 2033, driven by increasing demand for automated visual intelligence across manufacturing, retail, logistics, and security. Businesses using these solutions report measurable gains in operational efficiency, product quality, and decision-making accuracy, making computer vision not just a technological investment but a strategic differentiator.
By understanding how a computer vision solution works, executives can evaluate its potential to streamline operations, enhance product and service quality, and achieve a competitive edge turning visual intelligence into tangible business value.
Core components of a computer vision solution
A computer vision solution is built around a set of interdependent components that work together to transform visual information into actionable business insights. Understanding these core elements helps organizations effectively evaluate, implement, and optimize computer vision capabilities.
1. Visual data acquisition
At the foundation is the capture of high-quality visual data. Cameras, sensors, drones, and industrial imaging devices capture images or video streams of the real world. The quality, resolution, and positioning of these devices directly impact the accuracy and reliability of downstream analysis.
2. Data preprocessing and enhancement
Raw visual data often contains noise, distortions, or irrelevant information. Preprocessing prepares the data for analysis by cleaning, normalizing, and enhancing images adjusting brightness, contrast, resolution, or perspective to highlight relevant features. This step ensures consistent input quality and improves the precision of subsequent analysis.
3. Feature extraction
Feature extraction identifies and isolates critical visual patterns within an image, such as edges, shapes, textures, or color gradients. These features distill raw pixel data into meaningful representations that a system can interpret and use for decision-making. Accurate feature extraction is essential for detecting anomalies, monitoring quality, or tracking objects.
4. Pattern recognition and interpretation
Once features are extracted, the system interprets these patterns to identify objects, behaviors, or events. This step translates visual cues into structured insights—such as counting products on a conveyor belt, detecting defects, or analyzing customer movement in a retail environment. The interpretation layer converts data into information that can inform business decisions.
5. Actionable output and integration
The final component is delivering insights in a way that drives action. Visual intelligence is integrated into enterprise systems, dashboards, or alert mechanisms, enabling real-time decisions, operational adjustments, or predictive maintenance. The output is meaningful only when it connects to measurable business outcomes.
By combining these components, data acquisition, preprocessing, feature extraction, pattern recognition, and actionable output, a computer vision solution provides organizations with a structured, repeatable, and scalable way to convert visual data into measurable value.
How computer vision solutions work
Computer vision (CV) solutions enable machines to capture, process, and interpret visual information from images or video, transforming raw visuals into structured data that AI models can understand and act upon. On its own, computer vision does not make decisions; its core purpose is to extract meaningful patterns from unstructured visual inputs, preparing them for AI algorithms to generate actionable insights.
At the foundation, computer vision systems process raw images or video frames at the pixel level, analyzing color, intensity, texture, shape, and spatial relationships. This stage involves several key steps.
- Preprocessing: Raw visuals are normalized, filtered, and enhanced to reduce noise and standardize inputs for further analysis.
- Feature extraction: Algorithms detect edges, contours, textures, and motion, converting visual patterns into structured representations such as feature maps.
- Encoding & transformation: These extracted features are transformed into formats suitable for AI models, such as tensors for deep learning networks, preserving spatial and temporal information.
Modern computer vision solutions rely heavily on deep learning architectures. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) excel at encoding spatial patterns in images, while Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) or Transformer-based models capture temporal and contextual information in video streams. Crucially, CV’s role ends with structuring and encoding the visual data; the AI model then applies its algorithms to detect anomalies, classify objects, predict outcomes, or trigger automated actions. For example:
On a production line, a CNN can extract visual features from a product, but the AI model determines whether it meets quality standards and initiates alerts.
In retail, computer vision identifies customer movement patterns, while AI models interpret this data to optimize store layout, predict demand, or personalize recommendations.
The integration of computer vision and AI forms a continuous feedback loop: as AI models process more structured visual data, predictions improve, and computer vision systems are refined to detect features more accurately. This seamless collaboration turns complex, high-volume visual information into actionable intelligence, enabling organizations to optimize operations, enhance safety, improve customer experience, and achieve measurable business outcomes.
What’s driving businesses to adopt computer vision solutions
Organizations are capturing vast amounts of visual data across manufacturing floors, retail spaces, and operational facilities. Computer vision converts these streams into actionable intelligence, revealing patterns, predicting potential issues, and empowering leaders to make informed, proactive decisions.
Operational efficiency and automation
One of the primary drivers of computer vision adoption is the need to enhance operational efficiency. Businesses often face repetitive, labor-intensive tasks such as quality inspections, inventory management, and process monitoring. Computer vision automates these tasks with precision, reducing reliance on manual labor while accelerating throughput. By minimizing errors and bottlenecks, organizations can reallocate resources to higher-value activities, optimizing both time and cost.
Risk mitigation and compliance
Managing risk and ensuring regulatory compliance are critical for businesses across industries. Computer vision solutions enable early detection of anomalies, defects, and security or safety threats. In sectors such as manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics, even minor errors can result in significant financial and reputational damage. Computer vision provides consistent, automated monitoring that reduces operational risks and ensures adherence to industry regulations, protecting both assets and stakeholders.
Real-time decision making and data-driven insights
Businesses today need to make decisions quickly and accurately. Computer vision converts visual inputs into actionable insights in real time, empowering leaders to respond faster and more strategically. Whether monitoring production lines, tracking inventory, or analyzing customer behavior through visual cues, computer vision enables organizations to act on insights immediately, preventing minor issues from escalating and maintaining a competitive edge.
Customer experience and engagement
Modern customers expect personalized, interactive, and seamless experiences. Computer vision enhances customer engagement by enabling visual product search, augmented reality try-ons, and touchless service interactions. By integrating computer vision into customer-facing processes, businesses can differentiate themselves, increase satisfaction, and foster loyalty in competitive markets.
Competitive differentiation and digital transformation
Adopting computer vision is a strategic move for businesses looking to differentiate themselves and drive digital transformation. Organizations leveraging computer vision can modernize operations, introduce innovative services, and streamline decision-making processes. Integrating visual intelligence into products and workflows signals innovation leadership while keeping pace with competitors relying on traditional methods. Computer vision is, therefore a key pillar of broader digital transformation strategies.
Cost reduction
Cost efficiency is another significant driver for computer vision adoption. Automated inspection, defect detection, and process monitoring reduce labor costs, prevent operational errors, and eliminate expensive rework. Over time, these savings compound, making computer vision a financially compelling investment that delivers measurable value without compromising quality.
Scalability of operations
As businesses grow, manual processes can become bottlenecks. Computer vision allows organizations to scale operations efficiently, processing vast amounts of visual data without proportionally increasing resources. Whether analyzing millions of images for inventory management or monitoring multiple production sites, computer vision ensures consistent performance that grows with the business.
Industry-specific transformation
Different industries face unique challenges that computer vision can address. Retailers benefit from visual product recognition and inventory tracking, manufacturers from precise defect detection, and healthcare providers from medical image analysis. By solving industry-specific problems with tailored computer vision applications, businesses achieve operational excellence and innovation simultaneously.
Accuracy and consistency
Precision and reliability are core advantages of computer vision. Manual inspections and monitoring are prone to variability, fatigue, and human error. Computer vision delivers consistent, high-accuracy results, ensuring quality and operational integrity. In quality-sensitive industries, this consistency is not optional, it is essential for maintaining standards and trust.
The adoption of computer vision is driven by fundamental business imperatives: improving operational efficiency, mitigating risk, enabling real-time decision-making, enhancing customer engagement, and achieving competitive differentiation. These drivers are the core reasons why organizations are investing in computer vision today. Companies that embrace computer vision gain the agility, accuracy, and insights necessary to thrive in a rapidly evolving market, making it a strategic necessity rather than a technological luxury.
How computer vision solutions are applied across business functions
Computer vision is transforming industries by enabling organizations to automate operations, improve accuracy, and generate actionable insights. By leveraging AI-driven visual intelligence, businesses can make faster, more informed decisions while reducing operational risks. Below are key use cases in retail, manufacturing, and distribution, crafted with executive-level insights and depth.
1. Customer behavior analysis
Computer vision enables retailers to capture and analyze granular data on customer movements, interactions, and engagement patterns throughout the store. By interpreting foot traffic, dwell times, and product handling, businesses can uncover actionable insights into shopping behavior, preferences, and conversion drivers.
This data informs store layout optimization, targeted marketing, and merchandising strategies, increasing sales efficiency and customer satisfaction. Beyond operational improvements, the technology allows executives to make strategic decisions grounded in real-world behavior, ensuring that investments in space planning, staffing, and promotions yield measurable ROI.
The actionable intelligence generated from computer vision analytics transforms raw visual data into a business advantage, supporting both short-term optimization and long-term strategic planning.
2. Automated checkout and cashier-less stores
Computer vision has redefined transactional efficiency by enabling automated checkout systems that eliminate traditional cashier processes. By identifying products and tracking items in real time, these systems accelerate purchase processing while reducing human error and operational costs.
For executives, this translates into measurable labor savings, enhanced customer throughput, and improved overall satisfaction. The technology integrates with inventory management systems, ensuring accurate stock updates and minimizing shrinkage.
Beyond operational efficiency, computer vision-powered checkout solutions serve as a differentiator in highly competitive retail markets, signaling innovation and responsiveness to evolving consumer expectations. This capability allows businesses to scale operations without proportional increases in workforce, maintaining operational agility.
3. Inventory management and shelf monitoring
Maintaining optimal stock levels and accurate inventory records is critical for retail profitability. Computer vision automates shelf monitoring, identifying out-of-stock items, misplacements, and planogram compliance in real time.
Executives gain continuous visibility into inventory health, enabling proactive replenishment, reducing lost sales, and improving customer satisfaction. Beyond operational precision, this technology provides data-driven insights that influence supply chain decisions, promotional planning, and product lifecycle management.
By leveraging computer vision analytics, retail leaders can make informed decisions that align merchandising strategies with consumer demand patterns. The integration of visual intelligence into inventory workflows ensures accuracy, consistency, and scalability, reducing operational risk and enabling smarter resource allocation.
4. Loss prevention and security
Retail shrinkage remains a major challenge for organizations seeking sustainable profitability. Computer vision enhances loss prevention by monitoring store activity, detecting suspicious behavior, and identifying potential theft in real time. Advanced facial recognition and object tracking enable security teams to intervene promptly, while reducing reliance on manual observation.
For executives, this translates into measurable reductions in losses, improved operational efficiency, and enhanced customer trust. The system also provides audit trails and compliance-ready records, which are invaluable for corporate governance and risk management.
By embedding visual intelligence into security protocols, retail organizations create safer environments while reinforcing operational accountability and strategic oversight.
5. Quality control and defect detection
Product consistency and quality are critical to maintaining brand reputation and reducing returns. Computer vision automates inspection of manufactured goods at every stage of production, detecting defects, misalignments, and packaging errors with unparalleled accuracy. This ensures adherence to quality standards and reduces human error.
For executives, the benefits extend beyond operational efficiency; accurate quality control minimizes waste, decreases production costs, and protects brand equity. The technology enables predictive insights by identifying patterns that lead to recurring defects, informing process improvement initiatives.
By integrating computer vision into quality management workflows, manufacturing leaders can make data-driven decisions that align production performance with corporate objectives and customer expectations.
6. Predictive maintenance
Unplanned equipment downtime can severely impact productivity and profitability. Computer vision monitors machinery for visual indicators of wear, misalignment, or anomalies, enabling predictive maintenance before critical failures occur. This proactive approach reduces operational interruptions, extends asset life, and optimizes maintenance schedules.
For executives, predictive insights improve capital allocation, reduce repair costs, and increase production reliability. Additionally, integrating computer vision with analytics platforms supports strategic planning by identifying systemic issues across production lines.
By adopting visual intelligence for maintenance, manufacturers can ensure continuous operation, safeguard employee safety, and achieve measurable operational efficiency gains, translating into long-term cost savings and sustainable competitive advantage.
7. Process automation and compliance monitoring
Maintaining standardized manufacturing processes and regulatory compliance is essential for operational excellence. Computer vision monitors assembly lines, packaging, labeling, and safety protocols in real time, ensuring every step adheres to defined standards. This automation minimizes human error, accelerates production, and ensures compliance with industry regulations.
From an executive perspective, this capability reduces operational risk, protects against regulatory penalties, and supports governance initiatives. The data generated provides insights into process efficiency, bottlenecks, and potential improvements, enabling strategic decisions rooted in accurate, actionable intelligence.
Integrating computer vision into compliance and process management ensures operational reliability, regulatory adherence, and a foundation for continuous improvement.
8. Warehouse inventory tracking
Efficient distribution relies on accurate, real-time visibility of stock within warehouses and distribution centers. Computer vision tracks packages, pallets, and containers automatically, updating inventory records continuously. This reduces errors, accelerates order fulfillment, and optimizes storage utilization.
For executives, enhanced inventory visibility translates into better resource planning, reduced operational risk, and measurable cost savings. The insights generated enable proactive decision-making, such as prioritizing high-demand products or identifying bottlenecks. Integrating computer vision into warehouse management systems ensures operational accuracy and scalability, supporting both daily efficiency and long-term strategic planning for distribution networks.
9. Package inspection and verification
Ensuring product integrity throughout distribution is essential to meeting customer expectations and maintaining brand trust. Computer vision inspects packages for damage, verifies labeling accuracy, and confirms correct assembly before dispatch.
By automating these tasks, distribution centers minimize human error, reduce returns, and enhance operational throughput. From an executive perspective, this capability improves customer satisfaction, decreases operational risk, and provides actionable insights into recurring packaging issues.
The technology also supports compliance with handling standards and regulatory requirements, enabling informed strategic decisions on process improvements and supply chain resilience.
10. Handling compliance and condition monitoring
Computer vision monitors package orientation, stacking, and storage conditions to ensure that products are handled correctly throughout the distribution process. Mismanagement can result in damage, spoilage, or regulatory violations, leading to financial losses and reputational risk. For executives, deploying computer vision ensures operational accountability, reduces loss exposure, and provides data-driven insights for improving handling practices.
Visual intelligence enables monitoring at scale, capturing anomalies that human oversight may miss, and supporting strategic decisions for optimizing warehouse layout, packaging protocols, and handling procedures. This directly enhances the efficiency, reliability, and sustainability of distribution operations.
In retail, manufacturing, and distribution, computer vision adoption is driven by a clear need to optimize operations, reduce errors, ensure compliance, and generate actionable insights. By applying visual intelligence across customer interactions, production processes, and distribution workflows, businesses can make data-driven decisions that improve efficiency, reduce risk, and create measurable value.
These solutions empower executives to align operational performance with strategic objectives, enabling long-term growth and maintaining a competitive edge in increasingly complex and fast-paced markets.
Real‑world applications of computer vision solution
1. Amazon Go: Autonomous / Cashierless checkout
Amazon Go has revolutionized retail checkout by implementing a fully cashierless experience powered by computer vision technology. Ceiling-mounted cameras and shelf sensors continuously track customer interactions, capturing which products are picked up or returned. Advanced computer vision systems process this visual data in real time, updating the shopper’s virtual cart and charging accounts automatically upon exit.
Beyond eliminating queues, this approach streamlines computer vision tasks such as object detection, pose estimation, and instance segmentation, enabling precise recognition of products and their exact locations. Customers benefit from a seamless shopping experience, while the retailer gains higher basket sizes and improved revenue.
Accuracy rates exceed 99%, and regulators in some regions now recognize these automated transactions as valid. Amazon Go demonstrates how emerging technologies like vision transformers and generative AI can directly enhance operational efficiency, increase productivity, and elevate customer satisfaction, setting a benchmark for the next generation of retail innovation.
2. Walmart: Inventory and shelf monitoring
Walmart leverages computer vision systems to monitor inventory and ensure shelves are always stocked across its stores. Cameras and smart shelf sensors capture real-time digital images of products, which AI models analyze while analyzing visual data for empty shelves, misplaced items, or stock shortages.
Staff receive instant alerts to restock or correct errors, reducing out-of-stock events and helping optimize product placement. This automation transforms previously manual computer vision tasks, ensuring compliance with planograms and consistent product presentation.
By reducing human error and improving operational efficiency, Walmart’s CV adoption increases productivity and enhances the overall shopping experience. The integration of these current systems highlights how large-scale, real-time computer vision technology can deliver measurable business impact in retail.
3. Kroger: Customer analytics & queue management
Kroger uses computer vision technology to track foot traffic, queue lengths, and customer movement patterns within its stores. Overhead cameras capture live video streams, which AI models analyze to detect crowded aisles or forming queues, alerting staff to open additional registers or adjust staffing in real time.
Heatmaps derived from this analyzing visual data reveal popular product areas, engagement with in-store displays, and optimal product placement, helping managers make informed operational decisions. These systems can also integrate facial recognition to understand shopper demographics (while maintaining privacy standards), and even simulate scenarios for traffic lights or self-driving carts in future store automation.
Kroger’s implementation demonstrates how emerging technologies and advanced computer vision systems can combine real-time insights, instance segmentation, and predictive analytics to enhance operational efficiency, increase productivity, and deliver an improved, personalized customer experience.
Check how ready you are to deploy AI
agents and find out what you have in
place and what’s still needed!
Assess Now 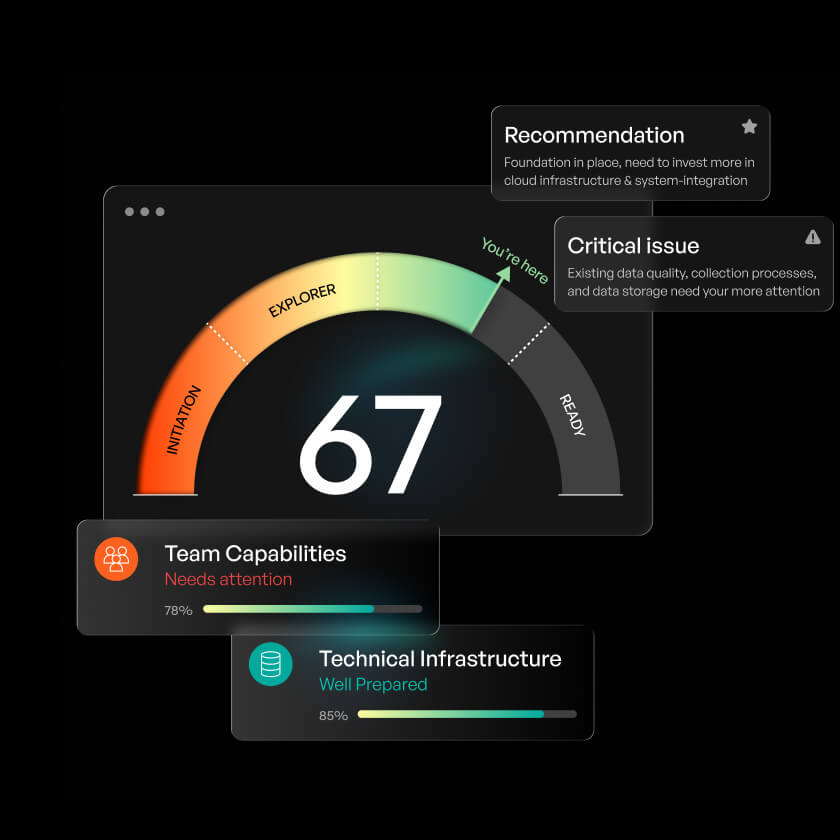
What it takes to make computer vision work for your business
Implementing a computer vision solution that drives measurable business impact requires more than just technology; it demands a strategic, structured approach that combines ai, machine learning, and deep learning algorithms with real-world operational understanding.
At the core, computer vision solutions transform digital images, video streams, and visual data into actionable insights, enabling organizations to improve product quality, operational efficiency, and decision-making at scale. However, achieving this impact requires careful planning, technical expertise, and collaboration with a technology partner who can guide the solution from concept to deployment.
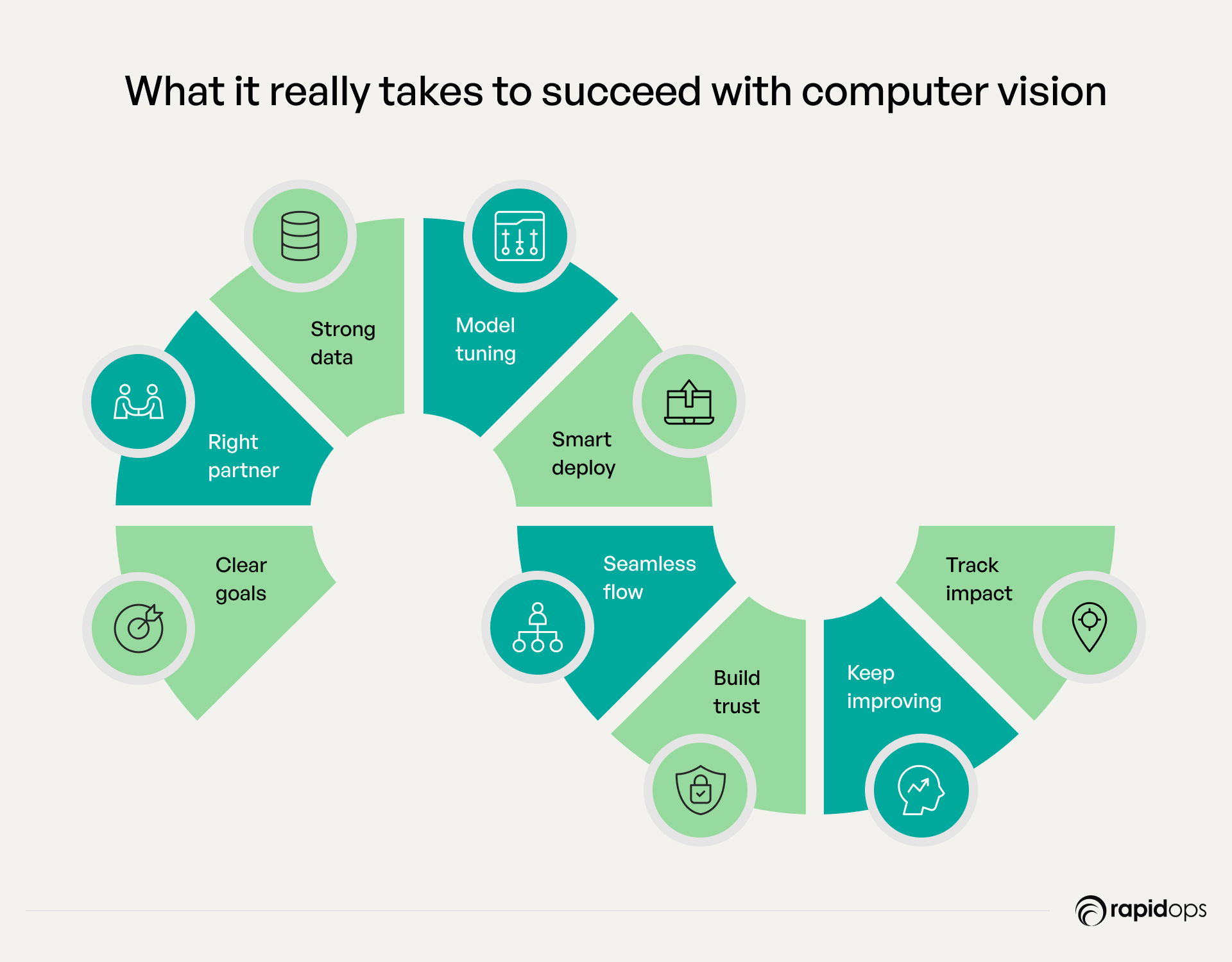
1. Define clear, measurable business outcomes
The first step in any successful computer vision project is anchoring it in specific business outcomes. Whether the goal is real-time monitoring of production processes, quality control on assembly lines, inventory accuracy, or understanding customer behavior in retail, clearly defining objectives ensures that every step, from selecting models to deploying cameras, is guided by measurable value. Business leaders must ask: what decisions or actions should the ai models enable? What metrics will determine success? By setting these parameters early, organizations avoid vague goals and ensure that computer vision contributes tangible ROI.
2. Engage a technology partner with domain expertise
No business can implement a sophisticated computer vision system alone. Partnering with a technology provider is critical for integrating computer vision algorithms, ai models, and computer vision platforms into existing workflows. A technology partner brings expertise in machine learning algorithms, deep learning, image recognition, object detection, pose estimation, and facial recognition, while also managing training data, model performance, and deployment constraints. They ensure that the system is scalable, reliable, and aligned with operational realities such as multiple cameras, edge devices, or cloud-based processing.
3. Curate high-quality, representative data
Data is the backbone of any computer vision system. High-fidelity, diverse datasets including video data, digital images, and visual elements, allow AI models to recognize patterns, classify objects, and detect anomalies accurately. Incorporating edge cases and rare scenarios ensures robust performance under real-world conditions.
For example, manufacturing computer vision relies on images from production processes and assembly lines to detect defects, while retail computer vision analyzes customer behavior and product placement for operational insights. Proper data annotation and quality control directly influence model accuracy and reliability.
4. Customize models and optimize performance
Pre-trained models can accelerate implementation, but achieving high precision often requires fine-tuning models, training with domain-specific data, or using hybrid deep learning algorithms. Tasks such as object tracking, image recognition, pose estimation, and visual inspection must be optimized for real-time detection and continuous monitoring, ensuring that insights are actionable and relevant. Technology partners guide this process, helping to reduce false positives, improve model performance, and maintain accuracy across huge volumes of visual data.
5. Deploy with real-world constraints in mind
A computer vision system’s effectiveness depends on deployment planning. Considerations include latency, hardware limitations, bandwidth, and whether inference occurs on existing cameras, edge devices, or in the cloud. Aligning computer vision systems with operational constraints ensures seamless integration into workflows without disruption. For example, remote monitoring of facilities or automated optical character recognition in logistics requires careful planning to balance real-time insights with resource efficiency.
6. Integrate AI insights into business workflows
The true value of computer vision lies in translating visual intelligence into action. AI vision models should feed insights directly into operational systems such as erp dashboards, maintenance alerts, or supply chain tools. This enables teams to optimize resource allocation, safety protocols, and product placement, while also improving customer satisfaction and inventory accuracy. Seamless integration ensures that the system enhances decision-making rather than remaining a siloed analytical tool.
7. Ensure explainability and build trust
Stakeholders must understand why the system makes certain predictions. Explainable ai, including techniques for facial recognition, object detection, and image processing tasks, fosters confidence and encourages adoption. Transparent dashboards and interpretability strengthen compliance and reduce resistance to ai-driven insights, ensuring that computer vision becomes a trusted part of the organization’s operational fabric.
8. Monitor, retrain, and continuously improve
A computer vision solution is never “set and forget.” continuous monitoring, retraining, and performance tracking ensure models adapt to changing environments, evolving video streams, and new visual data scenarios. Using computer vision platforms to automate retraining and manage model training and testing, organizations maintain high performance, detect anomalies early, and extract actionable insights reliably over time.
9. Measure business impact beyond accuracy
Finally, success is measured not by technical metrics alone, but by business outcomes. Track improvements in operational efficiency, product quality, customer satisfaction, and real-time decision-making. A well-implemented computer vision solution transforms visual intelligence into measurable gains, allowing enterprises to scale operations, reduce costs, and gain a competitive edge.
Unlock the power of computer vision for real business impact
As we’ve seen, computer vision transforms complex business operations by turning visual data into actionable intelligence, revealing previously hidden opportunities, and enabling faster, smarter decisions. From detecting empty shelves in retail to ensuring defect-free manufacturing and optimizing inventory in distribution, the benefits are tangible and measurable.
At Rapidops, we’ve guided enterprises in harnessing computer vision solutions to drive real business outcomes. Whether it’s real-time defect detection, automated visual inspection, workplace safety monitoring, asset tracking, or operational visibility, we help organizations build and deploy production-grade systems that work reliably in real-world environments.
Through our end-to-end implementation approach data preparation, model development, edge or cloud deployment, and integration into existing workflows, we enable companies to turn raw visual data into meaningful insights that improve efficiency, reduce operational errors, and strengthen decision-making at scale.
Ready to turn visual data into real business impact?
Schedule an appointment with one of our computer vision experts to explore how production-ready visual intelligence can streamline operations, improve efficiency, and keep you ahead of the competition.
Frequently Asked Questions
What types of data are required to train a computer vision solution?
To build accurate and effective computer vision solutions, businesses need high-quality, labeled visual datasets, including images, videos, and sometimes 3D scans. The data must capture real-world variations such as lighting, angles, and resolutions to ensure reliable model performance. Adding contextual metadata like timestamps, geolocation, or sensor readings can further enhance model intelligence. Properly curated datasets minimize bias, improve detection accuracy, and make the solution adaptable across business environments, from retail inventory monitoring to industrial quality inspection.
What is the difference between computer vision and AI?
While Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the broad discipline that enables machines to mimic human reasoning, computer vision solutions are a specialized branch of AI focused on interpreting visual data. These solutions analyze images and videos to extract actionable insights, detect patterns, and support decision-making. Unlike AI systems in natural language processing or predictive analytics, computer vision applies AI techniques to the visual domain, helping businesses automate processes such as product identification, security surveillance, or quality control.
Can computer vision solutions work in real-time environments?
Yes. Modern computer vision solutions are designed for real-time processing, leveraging edge computing, GPU acceleration, and optimized deep learning models. This enables instant analysis of video feeds or images to trigger automated actions or alerts. Real-time computer vision is essential in scenarios like autonomous retail checkout, live security monitoring, and industrial defect detection, where timely insights directly enhance operational efficiency, safety, and customer experience.
What are the biggest challenges in adopting computer vision technology?
Adopting computer vision solutions comes with several challenges. First, data quality and labeling are critical, poor or biased datasets reduce model performance. Integrating computer vision with existing IT systems and business workflows can be complex. Hardware requirements such as cameras and GPUs may also increase costs. Additionally, businesses must address privacy, compliance, and security concerns when handling sensitive visual data. Finally, ongoing model training, monitoring, and maintenance are required to ensure sustained accuracy in dynamic real-world conditions.
What emerging trends in computer vision should businesses prepare for in 2026?
In 2026, businesses will see multimodal computer vision solutions that combine image recognition with NLP and predictive analytics for richer insights. Edge-based AI processing will allow faster, low-latency operations, reducing dependency on cloud infrastructure. Synthetic data generation and generative AI will accelerate model training and overcome data limitations. Trends like AI-powered personalization, autonomous operations, and enhanced security analytics will expand, enabling organizations to automate complex workflows and improve efficiency, accuracy, and customer experience.
Can small and medium businesses benefit from computer vision, or is it only for large enterprises?
Absolutely. Small and medium businesses (SMBs) are leveraging computer vision solutions through cloud-based platforms, pre-trained AI models, and managed services that lower the barrier to entry. SMBs are leveraging these applications for inventory management, quality inspection, or customer analytics without heavy upfront investments. Scalable computer vision solutions help SMBs reduce operational costs, enhance productivity, and deliver superior customer experiences, enabling them to compete alongside larger enterprises in efficiency and innovation.

Saptarshi Das
Content Editor
9+ years of expertise in content marketing, SEO, and SERP research. Creates informative, engaging content to achieve marketing goals. Empathetic approach and deep understanding of target audience needs. Expert in SEO optimization for maximum visibility. Your ideal content marketing strategist.
What’s Inside
- Understanding computer vision solutions for business
- Core components of a computer vision solution
- How computer vision solutions work
- What’s driving businesses to adopt computer vision solutions
- How computer vision solutions are applied across business functions
- Real‑world applications of computer vision solution
- What it takes to make computer vision work for your business
- Unlock the power of computer vision for real business impact

Let’s build the next big thing!
Share your ideas and vision with us to explore your digital opportunities
Similar Stories
- Engineering
- undefined Mins
- September 2022

- Engineering
- undefined Mins
- January 2016

- Engineering
- 5 Mins
- November 2015


Receive articles like this in your mailbox
Sign up to get weekly insights & inspiration in your inbox.
